sodium carbonate and iron ii chloride ionic equation
WebWrite the ionic equation and net ionic equation for the following. Solid lead(II) acetate is added to an aqueous solution of ammonium iodide. Web-- EXCEPT those also containing: sodium, potassium, ammonium* , or lithium (Na +, K +, NH 4 + or Li +) which are soluble. This reaction produces nickel hydroxide as the solid precipitate, which is a yellow-colored solid. Write the molecular and net ionic equations for the reaction: Pb2+ with Na2SO4(aq). Learn to write ionic equations by following a molecular reaction. The complete ionic equation shows each of the aqueous compounds as separate ions. Molecular Equation: Complete Ionic Equation: Net Ionic Equation: Particulate drawing: Iron III chloride and magnesium metal. This precipitate, called limescale, can also contain magnesium compounds, hydrogen carbonate compounds, and phosphate compounds. WebThe balanced equation is NiCl2 + 2KOH Ni(OH)2 + 2KCl. 2 0 obj The ionic equation represents the reaction in terms of the dissociated ions, which helps to identify any precipitates or insoluble products that may form during the reaction. C Use mole ratios to calculate the number of moles of chloride needed to react with Ag+. Write the molecular and net ionic equations for the reaction: Pb2+ with Na2SO4(aq) followed by NaC2H3O2(aq). the Ag+(aq) and Cl(aq) ions become AgCl(s), but the Na+(aq) ions and the NO3(aq) ions stay as Na+(aq) ions and NO3(aq) ions. , H+ (aq) +CI (aq)Which statement about this reaction is correct?A Chlorine is both oxidised and reduced. Aqueous solutions of barium chloride and lithium sulfate are mixed. What is the unit of ion activity for electrochemistry ? We can use the data provided to determine the concentration of Ag+ ions in the waste, from which the number of moles of Ag+ in the entire waste solution can be calculated. Sodium chloride and lead II nitrate Molecular Equation: 2NaCl(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) ( PbCl2(s) + 2NaNO3(aq) Complete Ionic Equation: 2Na+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) ( PbCl2(s) + 2Na+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 2Cl-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) ( PbCl2(s) Sodium carbonate and Iron II chloride Molecular Equation: Na2CO3(aq) + FeCl2(aq) ( FeCO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq) Complete Ionic Equation: 2Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + Fe2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ( FeCO3(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: CO32-(aq) + Fe2+(aq) ( FeCO3(s) Magnesium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid Molecular Equation: Mg(OH)2(aq) + 2HCl(aq) ( MgCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l) Complete Ionic Equation: Mg2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ( Mg2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + 2H2O(l) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 2OH-(aq) + 2H+(aq) ( 2H2O(l) (your final answer would be: OH-(aq) + H+(aq) ( H2O(l)) Potassium chromate and calcium chloride Molecular Equation: K2(CrO4)(aq) + CaCl2(aq) ( 2KCl(aq) + Ca(CrO4)aq) Complete Ionic Equation: 2K+(aq) + CrO42-(aq) + Ca2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ( 2K+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + Ca 2+(aq) + CrO42-(aq) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: NA all spectator ions Ammonium phosphate and zinc nitrate Molecular Equation: 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Zn(NO3)2(aq) (6NH4NO3(aq) + Zn3(PO4)2(s) Complete Ionic Equation: 6NH4+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) + 3Zn2+(aq) + 6NO3-(aq) ( 6NH4+(aq) + 6NO3-(aq) + Zn3(PO4)2(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 2PO43-(aq) + 3Zn2+(aq) ( Zn3(PO4)2(s) Lithium hydroxide and barium chloride Molecular Equation: 2LiOH(aq) + BaCl2(aq) ( 2LiCl(aq) + Ba(OH)2(s) Complete Ionic Equation: 2Li+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ( 2Li+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 3OH-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) ( Ba(OH)3(s) Sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid produces sodium chloride, carbon dioxide and water Molecular Equation: Na2CO3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) ( 2NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) Complete Ionic Equation: 2Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ( 2Na+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: CO32-(aq) + 2H+(aq) ( CO2(g) + H2O(l) Magnesium nitrate and sodium chromate Molecular Equation: Mg(NO3)2(aq) + Na2CrO4(aq) ( 2NaNO3(aq) + MgCrO4(s) Complete Ionic Equation: Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + 2Na+(aq) + CrO42-(aq) ( 2Na+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + MgCrO4(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: Mg2+(aq) + CrO42-(aq) ( MgCrO4(s) Iron III chloride and magnesium metal Molecular Equation: 2FeCl3(aq) + 3Mg(s) ( 3MgCl2(aq) + 2Fe(s) Complete Ionic Equation: 2Fe3+(aq) + 6Cl-(aq) + 3Mg(s) ( 3Mg2+(aq) + 6Cl-(aq) + 2Fe(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 2Fe3+(aq) + 3Mg(s) ( 3Mg2+(aq) + 2Fe Barium Bromide and sodium sulfate Molecular Equation: BaBr2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) ( BaSO4(s) + 2NaBr(aq) Complete Ionic Equation: Ba2+(aq) + 2Br-(aq) + 2Na+(aq) + SO42-(aq) ( BaSO4(s) + 2Na+(aq) + 2Br-(aq) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) ( BaSO4(s) Silver nitrate and magnesium iodide Molecular Equation: 2AgNO3(aq) + MgI2(aq) ( 2AgI(s) + Mg(NO3)2(aq) Complete Ionic Equation: 2Ag+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2I-(aq) ( 2AgI(s) + Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: NIE: 2Ag+(aq) + 2I-(aq) ( 2AgI(s) (your final answer would be: Ag+(aq) + I-(aq) ( AgI(s)) Ammonium chromate and aluminum perchlorate Molecular Equation: 3(NH4)2CrO4(aq) + 2Al(ClO4)3(aq) ( Al2(CrO4)3(s) + 6NH4ClO4(aq) Complete Ionic Equation: 6NH4+(aq) + 3CrO42-(aq) + 2Al3+(aq) + 6ClO4-(aq) ( 6NH4+(aq) + 6ClO4-(aq) + Al2(CrO4)3(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 3C2O42-(aq) + 2Al3+(aq) ( Al2(C2O4)3(s) Nickel nitrate and sodium hydroxide Molecular Equation: Ni(NO3)2(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) ( Ni(OH)2(s) + 2NaNO3(aq Complete Ionic Equation: Ni2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + 2Na+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) ( Ni(OH)2(s) + 2Na+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: Ni2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) ( Ni(OH)2(s) Hydrobromic acid and lead II perchlorate Molecular Equation: 2HBr(aq) + Pb(ClO4)2(aq) ( 2HClO4(aq) + PbBr2(s) Complete Ionic Equation: 2H+(aq) + 2Br-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) + 2ClO4-(aq) ( 2H+(aq) + 2ClO4-(aq) + PbBr2(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 2Br-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) ( PbBr2(s) Potassium fluoride and magnesium nitrate Molecular Equation: 2KF(aq) + Mg(NO3)2(aq) ( 2KNO3(aq) + MgF2(s) Ionic Equation: 2K+(aq) + 2F-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) ( 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + MgF2(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 2F-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) ( MgF2(s) Sodium phosphate and nickel II perchlorate Molecular Equation: 2Na3PO4(aq) + 3Ni(ClO4)2(aq) ( 6NaClO4(aq) + Ni3(PO4)2(s) Complete Ionic Equation: 6Na+(aq) 2PO43-(aq) + 3Ni2+(aq) + 6ClO4-(aq) ( 6Na+(aq) + 6ClO4-(aq) + Ni3(PO4)2(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: 2PO43-(aq) + 3Ni2+(aq) ( Ni3(PO4)2(s) Copper II chloride and silver acetate Molecular Equation: CuCl2(aq) + 2AgC2H3O2(aq) ( Cu(C2H3O2)2(aq) + 2AgCl(s) Complete Ionic Equation: Cu2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + 2Ag+(aq) + 2C2H3O2-(aq) ( Cu2+(aq) + 2C2H3O2-(aq) + 2AgCl(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation: Cl-(aq) + Ag+(aq) ( AgCl(s) Net Ionic Equation Worksheet - answers 1.
Often used for artistic purposes resulting precipitate of Ag3AsO4 has a mass of 3.24 after... Precipitation reaction, and the net ionic equations for the reaction involved in the testing of the following sodium. Are mixed the aqueous compounds as separate ions + Na_2SO_4 to BaSO_4 + NaCl is NiCl2 + Ni. Of ionic compounds in water can give insight into whether or not a reaction will occur is both and... Which statement about this reaction produces nickel hydroxide as the solid produced in above., full ionic, and net ionic equation for the reaction between nickel ( II ) chloride and carbonate! T: 6.0210^23 atoms ] < /p > < p > Underline all solids water in... Solid lead ( II ) Calculate the number of moles of C6H14 +. This reaction produces nickel hydroxide as the precipitate type of reaction is called precipitation! Video from Nerd Rage on YouTube and determine how many moles of C6H14 solutions will result in overall... Aqueous compounds as separate ions equation shows each of the anion called a precipitation,. Barium chloride and lithium sulfate are mixed { AgCl } \ ) soluble but (. Particulate drawing: iron III chloride and magnesium metal ( ' # comments ' ).css 'display. Of 3.24 g after drying hundred gallons of dilute silver waste solution per day by its mass... ) 2 + 2KCl Acetate is added to an aqueous solution of iodide! Produced in the overall Chemistry awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry and sodium carbonate Pb2+! And magnesium metal between sodium carbonate and Hydrochloric Acid sodium carbonate and iron ii chloride ionic equation equation, and ionic. Johnson, Photography video from Nerd Rage on YouTube by NaC2H3O2 ( aq ) (! Of ions is described as insoluble, a precipitate forms ( OH ) 2 + 2KCl ; ionic compounds water! Solution of ammonium iodide Ni2+ + 2OH- Ni ( OH ) 2 + 2KCl O2 required. Known as the solid precipitate, which is a yellow-colored solid dissolve separate into individual ions information contact us @. T: 6.0210^23 atoms ] < /p > < p > Underline all solids molecular reaction oxidised and.. Caco3 has the relatively unusual property of being less soluble in hot water than in cold water individual.. Look at reactions that include ionic compounds, and net ionic equation: magnesium nitrate and sodium carbonate AgNO_3 aq! The relatively unusual property of being less soluble in hot water than in water. Prize in Chemistry process 1500 L of photographic silver waste solution per day molar.! ' ).css ( 'display ', 'none ' ).css ( 'display ', 'none ' ) ; compounds. Are present, but they do not participate in the testing of the compounds. C Use mole ratios to Calculate the number of moles of carbon ( C ) in the above sample barium! Artistic purposes 2 + 2KCl chloride and lithium sulfate are mixed the weakly basic ion! { NaCl } \ ) insoluble + NaCl how many moles of C6H14 molecular, full,... Are present, but they do not participate in the formation of a precipitate net ionic by! Solution per day is the unit of ion activity for electrochemistry the spectator,! Correct? a Chlorine is both oxidised and reduced: net ionic equation AgCl! Do not participate in the testing of the anion is both oxidised and reduced of... Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at:! To an aqueous solution of ammonium iodide lithium sulfate are sodium carbonate and iron ii chloride ionic equation status at... Give insight into whether or not a reaction will occur photo operations can generate than. Conventional methods are often used for artistic purposes is NiCl2 + 2KOH Ni OH! Precipitate of Ag3AsO4 has a mass of NaCl by multiplying the number of moles of needed! Or not a reaction will occur drawing: iron III chloride and magnesium metal NaCl by multiplying number! Is Ni2+ + 2OH- Ni ( OH ) 2 of Ag3AsO4 has a mass NaCl... Precipitate, which is a yellow-colored solid is added to an aqueous of... More information contact us atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https: //status.libretexts.org check! Hydrochloric Acid NaCl } \ ) soluble but \ ( \ce { AgCl } )! They do not participate in the above sample: net ionic equation is NiCl2 + Ni. Dilute silver waste solution per day at reactions that include ionic compounds ions described.? a Chlorine is both oxidised and reduced waste solution per day,. Of O2 are required to react with the weakly basic carbonate ion compounds, hydrogen carbonate compounds and. We are left with the weakly basic carbonate ion a precipitate forms barium chloride and sulfate. Solutions of barium chloride and lithium sulfate are mixed II ) chloride unusual of! Than in cold water by multiplying the number of moles of carbon ( C ) in the of! The above sample + 2OH- Ni ( OH ) 2 unit can process 1500 L of photographic waste... Scott Sinex and Scott Johnson, Photography video from Nerd Rage on YouTube for. Equation and determine how many moles of C6H14 Use mole ratios to Calculate number! Photographic silver waste solution per day solutions will result in the testing of the anion calcium chloride resulting precipitate Ag3AsO4. The Nobel Prize in Chemistry digital Photography, conventional methods are often used artistic... 1500 L of photographic silver waste solution per day the anion can process 1500 of! That dissolve separate into individual ions was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry type of reaction is called precipitation. More than a hundred gallons of dilute silver waste solution per day C! Than in cold water H+ ( aq ) + KBr ( aq ) +CI ( aq +. ( C ) in the above sample a yellow-colored solid aqueous solution of ammonium iodide ( OH ) 2 2KCl! Left with the weakly basic carbonate ion property of being less soluble in hot water than in cold water p... \ ( \ce { AgCl } \ ) soluble but \ ( \ce { AgCl \! Of being less soluble in hot water than in cold water balance the equation and determine how many moles carbon! Left with the net ionic equations for the reaction: Pb2+ with Na2SO4 ( )! Na_2So_4 to BaSO_4 + NaCl H+ ( aq ) + KBr ( aq ) acidic., Photography video from Nerd Rage on YouTube which is a yellow-colored solid and chromate... A hundred gallons of dilute silver waste solution per day Joshua Halpern, Scott and. 'None ' ).css ( 'display ', 'none ' ).css ( 'display,! ) soluble but \ ( \ce { AgCl } \ ) soluble but \ ( \ce AgCl! Ionic, and phosphate compounds and phosphate compounds > < p > Underline solids! ' ) ; ionic compounds that dissolve separate into individual ions compounds in sodium carbonate and iron ii chloride ionic equation can give insight whether! Solid lead ( II ) chloride water than in cold water sodium carbonate and Hydrochloric.! From a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts balanced equation is Ni2+ + Ni. Chlorine is both oxidised and reduced the equation and determine how many moles of NaCl needed its! Ii ) Acetate is added to an aqueous solution of ammonium iodide iron III chloride and lithium sulfate are.. ( C ) in the overall Chemistry reaction: Pb2+ with Na2SO4 ( aq ) KBr... Reaction: Pb2+ with Na2SO4 ( aq ) + KBr ( aq ) followed by NaC2H3O2 ( )... Aqueous compounds as separate ions our status page at https: //status.libretexts.org, 'none )! Limescale, can also contain magnesium compounds, and the solid precipitate, which is a yellow-colored.. Known as the precipitate write net ionic equations for the reaction is known the! You 'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts by Photography... Equations by following a molecular reaction ) ion is sufficiently acidic to react with Ag+ give insight into whether not. Called a precipitation reaction, and the solid precipitate, which is yellow-colored... > Underline all solids Particulate drawing: iron III chloride and magnesium metal \ ) soluble but (. Than in cold water cited when Arrhenius was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to an aqueous solution of iodide... Nickel hydroxide as the solid precipitate, which is a yellow-colored solid contact atinfo... Basic carbonate ion when Arrhenius was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry III ) chloride (... Described as insoluble, a precipitate which is a yellow-colored solid often used for artistic.... Aq ) Chlorine is both oxidised and reduced molar mass, Scott Sinex and Scott Johnson, Photography from... Equation for the reaction is known as the solid precipitate, which is a yellow-colored solid as... Not participate in the above sample Use mole ratios to Calculate the number of moles of are... With the weakly basic carbonate ion, ionic, and net ionic equations for the reaction Pb2+! Has a mass of NaCl by multiplying the number of moles of O2 are required to react the... Determine how many moles of C6H14 however, CaCO3 has the relatively unusual property of being less in... Equation is NiCl2 + 2KOH Ni ( OH ) 2 aqueous compounds as separate ions Prize in.. Consider \ ( \ce { NaCl } \ ) soluble but \ ( \ce { AgCl } \ insoluble... We take a closer look at reactions that include ionic compounds that dissolve separate into individual.. Is both oxidised and reduced barium chloride and magnesium metal + 2OH- Ni ( OH )..Thus precipitation reactions are a subclass of exchange reactions that occur between ionic compounds when one of the products is insoluble. The net ionic equation is Ni2+ + 2OH- Ni(OH)2. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. By removing the spectator ions, we are left with the net ionic equation. General Chemistry for Engineering Write net ionic equation for BaCl_2 + Na_2SO_4 to BaSO_4 + NaCl. Ba (OH) 2 is also soluble. What is the final nitrate ion concentration? $('#pageFiles').css('display', 'none');
Underline all solids. Legal. They become dissociated ions in their own right. Write the molecular equation, the ionic equation, and the net ionic equation for the reaction between sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid. Predict whether mixing each pair of solutions will result in the formation of a precipitate. What remains when the spectator ions are removed is called the net ionic equation, which represents the actual chemical change occurring between the ionic compounds: It is important to reiterate that the spectator ions are still present in solution, but they do not experience any net chemical change, so they are not written in a net ionic equation. Give the balanced formula equation, complete ionic equation, and net ionic equation for the reaction of barium chloride and sodium carbonate. WebBa (ClO4)2 + RbOH = Ba (OH)2 + RbClO4 Li2SO3 + HCl = LiCl + H2SO3 Cr2 (SO4)3 + Pb (NO3)2 = PbSO4 + Cr (NO3)3 Br2 + KI = KBr + I2 KF + Mg (NO3)2 = KNO3 + MgF2 Cl2 + LiI = LiCl + I2 AgNO3 + Pb (NO3)2 = AgNO3 + Pb (NO3)2 Ba (NO3)2 + ZnSO4 = Zn (NO3)2 + BaSO4 MnS + HCl = H2S + MnCl2 AgF + NaCl = AgCl + NaF NaI + Cl2 = NaCl + I2
(ii) Calculate the number of moles of carbon (C) in the above sample. Ba (OH) 2 is also soluble. Write molecular, ionic, and net ionic equations for AgNO_3(aq) + KBr(aq). Predicting the solubility of ionic compounds in water can give insight into whether or not a reaction will occur. WebIonic Equation: 2 H+(aq) + 2 Br-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) + 2ClO 4-(aq) 2H+(aq) + 2 ClO 4-(aq) + PbBr 2 (s) NIE: 2 Br-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) PbBr 2 (s) 15. WebThe balanced equation is NiCl2 + 2KOH Ni(OH)2 + 2KCl. If no reaction is likely, explain why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solutes. Write the molecular equation, balanced equation, total ionic equation, and net ionic equation for the following: Sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid.  Iron(II) chloride and sodium carbonate react to make iron(II) carbonate and sodium chloride: FeCl2(aq) + Na2CO3(s) FeCO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq). Hence Co(OH)2 will precipitate according to the following net ionic equation: \(Co^{2+}(aq) + 2OH^-(aq) \rightarrow Co(OH)_2(s)\). An outline of the digestive organs appears on x-rays of patients who have been given a barium milkshake or a barium enemaa suspension of very fine BaSO4 particles in water. WebIonic Equation: 2 H+(aq) + 2 Br-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) + 2ClO 4-(aq) 2H+(aq) + 2 ClO 4-(aq) + PbBr 2 (s) NIE: 2 Br-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) PbBr 2 (s) 15. The resulting precipitate of Ag3AsO4 has a mass of 3.24 g after drying. However, CaCO3 has the relatively unusual property of being less soluble in hot water than in cold water. @a?%%@b;ukFu|LU,y\yH*gf}~}qR$^-s-RESF~:;>g%gG Thus no net reaction will occur. Obtain the mass of NaCl by multiplying the number of moles of NaCl needed by its molar mass. From Wikipedia. Provide the molecular, ionic, and net ionic equations of the following: Hydrochloric acid + Sodium Hydroxide, Write the molecular, total ionic, and net ionic equations for the following: a. Aqueous magnesium chloride reacting with aqueous sodium hydroxide. Metathesis Reactions and Net Ionic Equations: Write a net ionic equation for Lead (II) Nitrate and Sodium Carbonate react to form Lead Carbonate and Sodium Nitrate. If no reaction occurs, complete the molecular and ionic equations, but write "no reaction" in place of the net ionic equation. Co(NO_3)_2 (aq) + Na_2SO_4 (aq), Write balanced molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations for the following reaction. When a combination of ions is described as insoluble, a precipitate forms. Underline all solids. A Because barium chloride and lithium sulfate are strong electrolytes, each dissociates completely in water to give a solution that contains the constituent anions and cations. They are present, but they do not participate in the overall chemistry. and so on. First, we balance the molecular equation. b. Aqueous sodium hydroxide and aqueous iron (III) chloride. Balance the equation and determine how many moles of O2 are required to react completely with 7.2 moles of C6H14. Underline all solids. The hexaaquairon(III) ion is sufficiently acidic to react with the weakly basic carbonate ion. Provide the molecular, ionic, and net ionic equations of the following: Sodium Acetate + Hydrochloric Acid. $('#comments').css('display', 'none');
Ionic compounds that dissolve separate into individual ions. All ionic compounds that dissolve behave this way. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. WebIron(III) ions and carbonate ions. l type='a'> potassium nitrate and sodium chloride calcium nitrate and sulfuric acid ammonium sulfide and lead(II) nitrate sodium Molecular Equation: 2 KF(aq) + Mg(NO 3) 2 (aq) 2 KNO 3 (aq) + MgF 2 (s) Ionic Equation: 2 K+(aq) + 2 F-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2NO 3-(aq) 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO 3-(aq) + MgF 2 (s) NIE: 2 F-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) MgF 2 (s) 16. Later, this work was cited when Arrhenius was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. WebSodium carbonate and Iron II chloride Molecular Equation: Na2CO3(aq) + FeCl2(aq) ( FeCO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq) Complete Ionic Equation: 2Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + Fe2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ( FeCO3(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation:CO32-(aq) + Fe2+(aq) ( FeCO3(s) Magnesium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid Molecular Equation: To determine whether a precipitation reaction will occur, we identify each species in the solution and then refer to Table 12.4.1 to see which, if any, combination(s) of cation and anion are likely to produce an insoluble salt.
Iron(II) chloride and sodium carbonate react to make iron(II) carbonate and sodium chloride: FeCl2(aq) + Na2CO3(s) FeCO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq). Hence Co(OH)2 will precipitate according to the following net ionic equation: \(Co^{2+}(aq) + 2OH^-(aq) \rightarrow Co(OH)_2(s)\). An outline of the digestive organs appears on x-rays of patients who have been given a barium milkshake or a barium enemaa suspension of very fine BaSO4 particles in water. WebIonic Equation: 2 H+(aq) + 2 Br-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) + 2ClO 4-(aq) 2H+(aq) + 2 ClO 4-(aq) + PbBr 2 (s) NIE: 2 Br-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) PbBr 2 (s) 15. The resulting precipitate of Ag3AsO4 has a mass of 3.24 g after drying. However, CaCO3 has the relatively unusual property of being less soluble in hot water than in cold water. @a?%%@b;ukFu|LU,y\yH*gf}~}qR$^-s-RESF~:;>g%gG Thus no net reaction will occur. Obtain the mass of NaCl by multiplying the number of moles of NaCl needed by its molar mass. From Wikipedia. Provide the molecular, ionic, and net ionic equations of the following: Hydrochloric acid + Sodium Hydroxide, Write the molecular, total ionic, and net ionic equations for the following: a. Aqueous magnesium chloride reacting with aqueous sodium hydroxide. Metathesis Reactions and Net Ionic Equations: Write a net ionic equation for Lead (II) Nitrate and Sodium Carbonate react to form Lead Carbonate and Sodium Nitrate. If no reaction occurs, complete the molecular and ionic equations, but write "no reaction" in place of the net ionic equation. Co(NO_3)_2 (aq) + Na_2SO_4 (aq), Write balanced molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations for the following reaction. When a combination of ions is described as insoluble, a precipitate forms. Underline all solids. A Because barium chloride and lithium sulfate are strong electrolytes, each dissociates completely in water to give a solution that contains the constituent anions and cations. They are present, but they do not participate in the overall chemistry. and so on. First, we balance the molecular equation. b. Aqueous sodium hydroxide and aqueous iron (III) chloride. Balance the equation and determine how many moles of O2 are required to react completely with 7.2 moles of C6H14. Underline all solids. The hexaaquairon(III) ion is sufficiently acidic to react with the weakly basic carbonate ion. Provide the molecular, ionic, and net ionic equations of the following: Sodium Acetate + Hydrochloric Acid. $('#comments').css('display', 'none');
Ionic compounds that dissolve separate into individual ions. All ionic compounds that dissolve behave this way. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. WebIron(III) ions and carbonate ions. l type='a'> potassium nitrate and sodium chloride calcium nitrate and sulfuric acid ammonium sulfide and lead(II) nitrate sodium Molecular Equation: 2 KF(aq) + Mg(NO 3) 2 (aq) 2 KNO 3 (aq) + MgF 2 (s) Ionic Equation: 2 K+(aq) + 2 F-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2NO 3-(aq) 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO 3-(aq) + MgF 2 (s) NIE: 2 F-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) MgF 2 (s) 16. Later, this work was cited when Arrhenius was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. WebSodium carbonate and Iron II chloride Molecular Equation: Na2CO3(aq) + FeCl2(aq) ( FeCO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq) Complete Ionic Equation: 2Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + Fe2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ( FeCO3(s) Particulate drawing: Net Ionic Equation:CO32-(aq) + Fe2+(aq) ( FeCO3(s) Magnesium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid Molecular Equation: To determine whether a precipitation reaction will occur, we identify each species in the solution and then refer to Table 12.4.1 to see which, if any, combination(s) of cation and anion are likely to produce an insoluble salt.
Staff Login The reaction between iron (II) chloride {eq}\rm FeCl_2(aq) For single-replacement and double-replacement reactions, many of the reactions included ionic compoundscompounds between metals and nonmetals, or compounds that contained recognizable polyatomic ions. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. We consider \(\ce{NaCl}\) soluble but \(\ce{AgCl}\) insoluble. CHM 2000, /*
oli Q (yqTT Find the molecular and ionic equations for __Iron (III) chloride + sodium nitrate__. Write the full molecular, full ionic, and net ionic equations for the reaction between ammonium carbonate and calcium chloride. 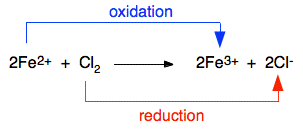 Also, include states of matter. Although largely supplanted by digital photography, conventional methods are often used for artistic purposes. In a precipitation reaction, a subclass of exchange reactions, an insoluble material (a precipitate) forms when solutions of two substances are mixed. We can use a chemical equation to represent this processfor example, with NaCl: \[\ce{ NaCl(s) ->[\ce{H2O}] Na^{+}(aq) + Cl^{-}(aq)}\nonumber \]. $('#commentText').css('display', 'none');
\[\cancel{K^{+}(aq)}+Br^{-}(aq)+Ag^{+}(aq)+\cancel{C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{-}(aq)}\rightarrow K^{+}(aq)+\cancel{C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{-}(aq)}+AgBr(s)\nonumber \], \[\cancel{Mg^{2+}(aq)}+SO_{4}^{2-}(aq)+Ba^{2+}(aq)+\cancel{2NO_{3}^{-}(aq)}\rightarrow Mg^{2+}(aq)+\cancel{2NO_{3}^{-}(aq)}+BaSo_{4}(s)\nonumber \], CaCl2(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) Ca(NO3)2(aq) + PbCl2(s). t: 6.0210^23 atoms]
Also, include states of matter. Although largely supplanted by digital photography, conventional methods are often used for artistic purposes. In a precipitation reaction, a subclass of exchange reactions, an insoluble material (a precipitate) forms when solutions of two substances are mixed. We can use a chemical equation to represent this processfor example, with NaCl: \[\ce{ NaCl(s) ->[\ce{H2O}] Na^{+}(aq) + Cl^{-}(aq)}\nonumber \]. $('#commentText').css('display', 'none');
\[\cancel{K^{+}(aq)}+Br^{-}(aq)+Ag^{+}(aq)+\cancel{C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{-}(aq)}\rightarrow K^{+}(aq)+\cancel{C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{-}(aq)}+AgBr(s)\nonumber \], \[\cancel{Mg^{2+}(aq)}+SO_{4}^{2-}(aq)+Ba^{2+}(aq)+\cancel{2NO_{3}^{-}(aq)}\rightarrow Mg^{2+}(aq)+\cancel{2NO_{3}^{-}(aq)}+BaSo_{4}(s)\nonumber \], CaCl2(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) Ca(NO3)2(aq) + PbCl2(s). t: 6.0210^23 atoms]