cataclastic metamorphism
Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. 
Metamorphism can also occur when rocks grind together, producing dynamic metamorphism, also called cataclastic metamorphism. High P/T Metamorphic Rocks, Metamorphism of Carbonate Rocks: University of Wisconsin Green Bay, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Metamorphism&oldid=1147063447, Short description is different from Wikidata, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 28 March 2023, at 16:44.  respectively and you should be aware that this has nothing to do with . During metamorphism of basalt to eclogite in subduction zones, hydrous minerals break down, producing copious quantities of water. It is usually light in colour, but it can be quite dark. At an oceanic spreading ridge, recently formed oceanic crust of gabbro and basalt is slowly moving away from the plate boundary (Figure 10.26). Recrystallization to coarser crystals reduces the surface area and so minimizes the surface energy.
respectively and you should be aware that this has nothing to do with . During metamorphism of basalt to eclogite in subduction zones, hydrous minerals break down, producing copious quantities of water. It is usually light in colour, but it can be quite dark. At an oceanic spreading ridge, recently formed oceanic crust of gabbro and basalt is slowly moving away from the plate boundary (Figure 10.26). Recrystallization to coarser crystals reduces the surface area and so minimizes the surface energy. 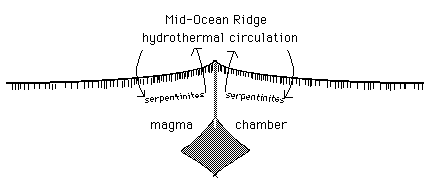 crystallize thus changing its chemistry. Kyanite is stable at surface conditions.
crystallize thus changing its chemistry. Kyanite is stable at surface conditions.  To the unaided eye, metamorphic changes may not be apparent at all. Cataclastic metamorphism is generally localized along fault planes (areas of detachment where rocks slide past one another).
To the unaided eye, metamorphic changes may not be apparent at all. Cataclastic metamorphism is generally localized along fault planes (areas of detachment where rocks slide past one another).
[40], Burial metamorphism takes place simply through rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. WebCataclastic metamorphism occurs along faults due to the frictional heating and deformation associated with the faulting. Dikes generally have small aureoles with minimal metamorphism, extending not more than one or two dike thicknesses into the surrounding rock,[50] whereas the aureoles around batholiths can be up to several kilometers wide. nose dive, they will heat up and metamorphose. Staurolite, kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition migmatite or migmatite gneiss. The difference in composition between an existing rock and the invading fluid triggers a set of metamorphic and metasomatic reactions. [26], Examples of dehydration reactions that release water include:[27], An example of a decarbonation reaction is:[28], In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. The heated water reacts of the neighboring rock called contact metamorphism. Migmatites are named by prefixing the rock name of the granitic material The fluids eventually escape through vents on the ocean floor known as black smokers. [61] The patterns of this hydrothermal alteration are used as a guide in the search for deposits of valuable metal ores. The resulting arc volcanoes tend to produce dangerous eruptions, because their high water content makes them extremely explosive. Textures produced by such adjustments range from breccias composed of angular, shattered rock fragments to very fine-grained, granulated or powdered rocks with obvious foliation and lineation. Web7.3.2 Flazer cataclasite Flazer cataclasite is a cataclastic metamorphic rock consisting of angular clasts within a fine-grained matrix formed by brittle fragmentation due to extreme kinetic shearing. These reactions are possible because of rapid diffusion of atoms at elevated temperature. Today, we will consider what happens when stuff goes down the tubes, gets metamorphosed and The collision zone becomes a belt of mountain formation called an orogeny. Rocks formed by contact metamorphism may not present signs of strong deformation and are often fine-grained[46][47] and extremely tough. A magma consists mostly of liquid rock matter, but may contain crystals of various minerals, and may contain a gas phase that may be dissolved in the liquid or may be present as a separate gas phase. Near the surface in A special type of metamorphism takes place under these very high-pressure but relatively low-temperature conditions, producing an amphibole mineral known as glaucophane (Na2(Mg3Al2)Si8O22(OH)2). . environmental variables can result in metamorphism. host rock, the contact zone heats up considerably. Different minerals will form depending on the exact temperature and the nature of the country rock.
garnite schist. Granulites form at crustal depths, typically during regional metamorphism at high thermal gradients of greater than 30 C/km. 0000007424 00000 n migmatite, injection gneiss, or lit-par-lit gneiss) or by differential fusion. The movement of rock causes a large amount of mineral water biochemical processes, An example of a synthetic material is the one referred to as quartz, which includes ground-up quartz crystals as well as resin. The rocks are typical of mechanical shear Prograde metamorphism results in rock characteristic of the maximum pressure and temperature experienced.
WebMechanical Metamorphism Cataclastic These rocks are formed by crushing and shearing with only minor recrystallization. X4C,hf:YpOMq{G40EtMBw~jh{'uq3InOVa3 rf^ !Hd7. in them. [69], There is considerable evidence that cataclasites form as much through plastic deformation and recrystallization as brittle fracture of grains, and that the rock may never fully lose cohesion during the process. Mylonite: finely ground, foliate For instance, the small calcite crystals in the sedimentary rocks limestone and chalk change into larger crystals in the metamorphic rock marble. Marble lacks platy minerals and is generally not foliated, which allows its use as a material for sculpture and architecture. Metasomatism takes place in some rocks adjacent to igneous intrusions (see Contact (thermal) metamorphism; Skarn). [54] Fluorine-rich magmatic waters which leave a cooling granite may often form greisens within and adjacent to the contact of the granite. The more silica, the lighter the color. [38] The conditions within the subducting slab as it plunges toward the mantle in a subduction zone produce their own distinctive regional metamorphic effects, characterized by paired metamorphic belts. Rocks subject to great heat are often changed, for example, limestone becomes marble, shale or mudstone becomes slate. 0000001807 00000 n 0000001291 00000 n [75] However, this is not universally accepted. What does it mean if something is suspenseful? Rocks formed under such environment are usually strongly foliated, such as slates, schists, and gniesses. where temperature and pressure are high enough for the rocks to deform plastically (ductile deformation). Also, water and other gases make bubbles in the magma, contributing Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). When extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the result is a shock wave. [83], The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. A more accurate idea of PT conditions can be gotten by considering a Gneiss usually is distinguished from schist by its foliation and schistosity; gneiss displays a well-developed foliation and a poorly developed schistosity and cleavage. Most of them, however, are foliate. 0000009149 00000 n Our editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article. Chemical reactions digest the minerals of the protolith which yields new minerals. This is a process known as quantity. [89][90] Because of the difficulty of depicting more than three components (as a ternary diagram), usually only the three most important components are plotted, though occasionally a compatibility diagram for four components is plotted as a projected tetrahedron.[92]. Increasing silica not only makes magmas lighter (in color), but makes When they can be recognized as "mixed rock," they are called [30] It most often refers to dynamothermal metamorphism, which takes place in orogenic belts (regions where mountain building is taking place),[31] but also includes burial metamorphism, which results simply from rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. WebRegional metamorphism is associated with the major events of Earth dynamics, and the vast majority of metamorphic rocks are so produced. Mylonites form Mineralogical changes occurring on a fault plane provide an obvious example. Metasomatism refers to the process whereby a preexisting igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rock undergoes compositional and mineralogical transformations associated with chemical reactions triggered by the reaction of fluids (so-called metasomatic agents), which invade the protolith. The collisions result in the formation of long mountain ranges, like those along the western coast of North America. In its lowest temperature/pressure form, this change is Burial metamorphism tends to produced low-grade metamorphic rock. Updates? degrees C (1998). Textures of metamorphic rocks crystalloblastic, xenoblastic and idioblastic. but are stable at different PT conditions (like graphite and diamond). In view of the tectonic importance of transform faults, a brief review of cataclastic rocks and particularly of those related to transform faults will be given in this chapter. Types, Grade, and Facies of Metamorphism, Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 3. Recrystallization will tend to align themselves such that the fabric formsperpendicular to * Serpentine is a product of hydrothermal alteration which some authorities the journey of that particular crustal package up and down the tectonic Mylonites contain porphyroclasts. About Equal Proportions of Light-colored and Dark-colored Minerals, Muscovite, Sericite, Sillimanite, Kyanite, Cordierite, Tremolite, index minerals. [56][57], Fenitization, or Na-metasomatism, is a distinctive form of contact metamorphism accompanied by metasomatism. Pressures in the lower mantle start at 24 GPa (GigaPascals), and climb to 136 GPa at the core-mantle boundary, so the impact is like plunging the rock deep into the mantle and releasing it again within seconds. 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. remaining melt changes from a more mafic to a more felsic melt; thus, if deep in the crust granites melt at about half the temperature that basalts do. Wollastonite, Albite, Andalusite, Garnet, Phlogopite, Diopside, Enstatite, only minor recrystallization. in book). The reaction is:[23], Many complex high-temperature reactions may take place between minerals without them melting, and each mineral assemblage produced provides us with a clue as to the temperatures and pressures at the time of metamorphism. [8] The solidus temperature depends on the composition of the rock, the pressure, and whether the rock is saturated with water. [45] Contact metamorphic rocks are usually known as hornfels. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred. weight of the overlying rock. Webcrystalline or glassy rock that forms from cooling of a magma. Webcataclastic metamorphism. Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist. ordinary crust, the temperature rises some 30 degrees per kilometer. metamorphism.