Perhaps the most important test of a materials mechanical response is the tensile test(Stress-strain testing, as well as almost all experimental procedures in mechanics of materials, is detailed by standards-setting organizations, notably the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). As the induced strain increases, these spherulites are first deformed in the straining direction. This implies that; = Engineering Stress The analytical equations for converting engineering stress-strain to true stress-strain are given below: In Abaqus the following actions are required for converting engineering data to true data, given that the engineering stress However, they are not without some subtlety, especially in the case of ductile materials that can undergo sub- stantial geometrical change during testing. (Definition, Types, Examples).
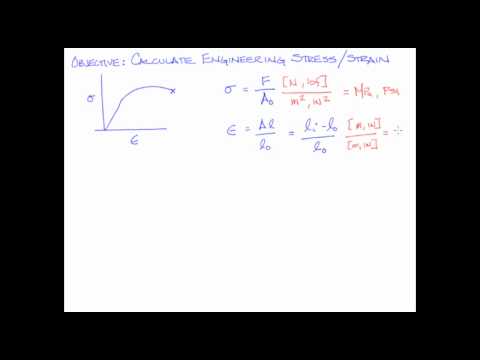 After the ultimate tensile strength, the true stress-strain curve can only be determined experimentally. When the stress e is plotted against the strain \(\epsilon_e\), an engineering stress-strain curve such as that shown in Figure 2 is obtained. These values are also referred to as nominal stress and strain. Unless otherwise stated, the stresses and strains referred to in all of the following are true (von Mises) values. 5 steps of FEA results verification Check the shape of deformations. Biaxial bulge testing has been used to determine stress-strain curves beyond uniform elongation. Otherwise, be a good engineer and accept this as our starting point! However, a complete true stress-strain curve could be drawn if the neck area were monitored throughout the tensile test, since for logarithmic strain we have, \[\dfrac{L}{L_0} = \dfrac{A}{A_0} \to \epsilon_t = \ln \dfrac{L}{L_0} = \ln \dfrac{A}{A_0}\]. From Equation 1.4.6, the engineering stress corresponding to any value of true stress is slope of a secant line drawn from origin (, not ) to intersect the curve at . Next we right click on the respectful data set and select process. To convert from true stress and strain to engineering stress and strain, we need to make two assumptions. This plasticity requires a mechanism for molecular mo- bility, which in crystalline materials can arise from dislocation motion (discussed further in a later module.) Show that the UTS (engineering stress at incipient necking) for a power-law material (Equation 1.4.8) is, \[\sigma_f = \dfrac{An^n}{e^n}\nonumber\]. WebEngineering stress and true stress are common ways of measuring load application over a cross-sectional area. Prior to necking, when the strain is still uniform along the specimen length, this volume constraint can be written: \[dV = 0 \to AL = A_0 L_0 \to \dfrac{L}{L_0} =\dfrac{A}{A_0}\]. Moreover, these concepts serve in highlighting the stress-strain relationship in a structure or member from the onset of loading until eventual failure. The Yield point can be clearly seen as well as the plastic region and fracture point (when the specimen breaks). where Y is the yield stress and K is the work hardening coefficient. The above discussion is concerned primarily with simple tension, i.e. (Properties, Applications, and Metallurgy), Why Mercury is Used in Thermometers (and Modern Alternatives), Definitions of Engineering and True Stress-Strain Curves. True Stress Strain Curve? The term modulus is used because the units of strain energy per unit volume are \(N-m/m^3\) or \(N/m^2\), which are the same as stress or modulus of elasticity.
After the ultimate tensile strength, the true stress-strain curve can only be determined experimentally. When the stress e is plotted against the strain \(\epsilon_e\), an engineering stress-strain curve such as that shown in Figure 2 is obtained. These values are also referred to as nominal stress and strain. Unless otherwise stated, the stresses and strains referred to in all of the following are true (von Mises) values. 5 steps of FEA results verification Check the shape of deformations. Biaxial bulge testing has been used to determine stress-strain curves beyond uniform elongation. Otherwise, be a good engineer and accept this as our starting point! However, a complete true stress-strain curve could be drawn if the neck area were monitored throughout the tensile test, since for logarithmic strain we have, \[\dfrac{L}{L_0} = \dfrac{A}{A_0} \to \epsilon_t = \ln \dfrac{L}{L_0} = \ln \dfrac{A}{A_0}\]. From Equation 1.4.6, the engineering stress corresponding to any value of true stress is slope of a secant line drawn from origin (, not ) to intersect the curve at . Next we right click on the respectful data set and select process. To convert from true stress and strain to engineering stress and strain, we need to make two assumptions. This plasticity requires a mechanism for molecular mo- bility, which in crystalline materials can arise from dislocation motion (discussed further in a later module.) Show that the UTS (engineering stress at incipient necking) for a power-law material (Equation 1.4.8) is, \[\sigma_f = \dfrac{An^n}{e^n}\nonumber\]. WebEngineering stress and true stress are common ways of measuring load application over a cross-sectional area. Prior to necking, when the strain is still uniform along the specimen length, this volume constraint can be written: \[dV = 0 \to AL = A_0 L_0 \to \dfrac{L}{L_0} =\dfrac{A}{A_0}\]. Moreover, these concepts serve in highlighting the stress-strain relationship in a structure or member from the onset of loading until eventual failure. The Yield point can be clearly seen as well as the plastic region and fracture point (when the specimen breaks). where Y is the yield stress and K is the work hardening coefficient. The above discussion is concerned primarily with simple tension, i.e. (Properties, Applications, and Metallurgy), Why Mercury is Used in Thermometers (and Modern Alternatives), Definitions of Engineering and True Stress-Strain Curves. True Stress Strain Curve? The term modulus is used because the units of strain energy per unit volume are \(N-m/m^3\) or \(N/m^2\), which are the same as stress or modulus of elasticity.  Although these dimensional changes are not considered in determining the engineering stress, they are of primary importance when determining true stress. At the UTS the differential of the load \(P\) is zero, giving an analytical relation between the true stress and the area at necking: \[P = \sigma_t A \to dP = 0 = \sigma_t dA + A d \sigma_t \to -\dfrac{dA}{A} = \dfrac{d\sigma_t}{\sigma_t}\]. This page titled 5.3: True and Nominal Stresses and Strains is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Dissemination of IT for the Promotion of Materials Science (DoITPoMS). where is the stress, is the applied force, and is the original cross-sectional area. Develop the relations given in Equation 1.4.6: \[\sigma_t = \sigma_e (1 + \epsilon_e) =\sigma_e \lambda, \epsilon_t = \ln (1 + \epsilon_e) = \ln \lambda \nonumber\]. Also remember, these equations are only valid before necking begins. Yield Stress, Yield Strength, and Yield Point, Elasticity and Youngs Modulus (Theory, Examples, and Table of Values), True Stress-Strain vs Engineering Stress-Strain, Stress, Strain, and the Stress-Strain Curve, What Are Shape Memory Alloys? True stress and true strain provide a much better representation of how the material behaves as it is being deformed, which explains its use in computer forming and crash simulations. These differ in the number of tangent points that can be found for the secant line, and produce the following yield characteristics: (a) No tangents: Here the curve is always concave upward as in part (a) of Figure 10, so the slope of the secant line rises continuously. In other words. This nonlinearity is usually as- sociated with stress-induced plastic flow in the specimen. Similarly, the true strain can be written T = L L0dL L = ln( L L0) = ln(1 + N) Brittle materials usually fracture(fail) shortly after yielding-or even at yield points- whereas alloys and many steels can extensively deform plastically before failure. All of this information can be found elsewhere on the site, but here is a quick reference sheet if you want to study the basic crystals quickly before an exam. Understanding true stress and true strain helps to address the need for additional load after the peak strength is reached. This is why the equation doesnt work after necking. (Crystal Structure, Properties, Interstitial Sites, and Examples), Double Hexagonal Close-Packed (La-type) Unit Cell, Close-Packed Rhombohedral (Sm-type) Unit Cell, 17 Metals With the Highest Melting Points (and Why), Refractory Metals (Definition, Examples, and Applications), What Are Superalloys? The polymer, however, differs dramatically from copper in that the neck does not continue shrinking until the specimen fails. True Strain The true strain (e) is defined as the instantaneous elongation per unit length of the specimen. The stress-strain curve for brittle materials are typically linear over their full range of strain, eventually terminating in fracture without appreciable plastic flow. This blog focuses on the difference between Engineering Stress-Strain and True Stress-Strain. (Applications, History, and Metallurgy), Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs): Materials, Manufacturing Methods, and Applications, Hastelloy C-276 (Composition, Properties, and Applications), Magnetic Materials: Types of Magnetism, Applications, and Origin of Magnetism, Which Metals Are Magnetic? WebTrue stress true strain curves of low carbon steel can be approximated by the Holloman relationship: = Kn where true stress = ; true strain = , n is the n-value (work hardening exponent or strain hardening exponent), and the K-value is the true stress at a true strain value of 1.0 (called the Strength Coefficient). But remember, this strain hardening expression is only valid between the yield strength and ultimate tensile strength. What are Alloys? In the absence of molecular slip and other mechanisms for energy dissipation, this mechanical energy is stored reversibly within the material as strain energy. For an applied force F and a current sectional area A, conserving volume, the true stress can be written T = F A = FL A0L0 = F A0(1 + N) = N(1 + N) where n is the nominal stress and N is the nominal strain. There are some practical difficulties in performing stress-strain tests in compression. For this material, determine (a) Youngs modulus, (b) the 0.2% offset yield strength, (c) the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS), (d) the modulus of resilience, and (e) the modulus of toughness. True stress correctly accounts for the changing cross-sectional area. (b) One tangent: The curve is concave downward as in part (b) of Figure 10, so a secant line reaches a tangent point at \(\lambda = \lambda_Y\). Your email address will not be published. In other words, Second, we need to assume that the strain is evenly distributed across the And so the engineering stress Is based on the initial cross-sectional area of our specimen. Engineering stress reaches a maximum at the Tensile Strength, which occurs at an engineering strain equal to Uniform Elongation.
Although these dimensional changes are not considered in determining the engineering stress, they are of primary importance when determining true stress. At the UTS the differential of the load \(P\) is zero, giving an analytical relation between the true stress and the area at necking: \[P = \sigma_t A \to dP = 0 = \sigma_t dA + A d \sigma_t \to -\dfrac{dA}{A} = \dfrac{d\sigma_t}{\sigma_t}\]. This page titled 5.3: True and Nominal Stresses and Strains is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Dissemination of IT for the Promotion of Materials Science (DoITPoMS). where is the stress, is the applied force, and is the original cross-sectional area. Develop the relations given in Equation 1.4.6: \[\sigma_t = \sigma_e (1 + \epsilon_e) =\sigma_e \lambda, \epsilon_t = \ln (1 + \epsilon_e) = \ln \lambda \nonumber\]. Also remember, these equations are only valid before necking begins. Yield Stress, Yield Strength, and Yield Point, Elasticity and Youngs Modulus (Theory, Examples, and Table of Values), True Stress-Strain vs Engineering Stress-Strain, Stress, Strain, and the Stress-Strain Curve, What Are Shape Memory Alloys? True stress and true strain provide a much better representation of how the material behaves as it is being deformed, which explains its use in computer forming and crash simulations. These differ in the number of tangent points that can be found for the secant line, and produce the following yield characteristics: (a) No tangents: Here the curve is always concave upward as in part (a) of Figure 10, so the slope of the secant line rises continuously. In other words. This nonlinearity is usually as- sociated with stress-induced plastic flow in the specimen. Similarly, the true strain can be written T = L L0dL L = ln( L L0) = ln(1 + N) Brittle materials usually fracture(fail) shortly after yielding-or even at yield points- whereas alloys and many steels can extensively deform plastically before failure. All of this information can be found elsewhere on the site, but here is a quick reference sheet if you want to study the basic crystals quickly before an exam. Understanding true stress and true strain helps to address the need for additional load after the peak strength is reached. This is why the equation doesnt work after necking. (Crystal Structure, Properties, Interstitial Sites, and Examples), Double Hexagonal Close-Packed (La-type) Unit Cell, Close-Packed Rhombohedral (Sm-type) Unit Cell, 17 Metals With the Highest Melting Points (and Why), Refractory Metals (Definition, Examples, and Applications), What Are Superalloys? The polymer, however, differs dramatically from copper in that the neck does not continue shrinking until the specimen fails. True Strain The true strain (e) is defined as the instantaneous elongation per unit length of the specimen. The stress-strain curve for brittle materials are typically linear over their full range of strain, eventually terminating in fracture without appreciable plastic flow. This blog focuses on the difference between Engineering Stress-Strain and True Stress-Strain. (Applications, History, and Metallurgy), Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs): Materials, Manufacturing Methods, and Applications, Hastelloy C-276 (Composition, Properties, and Applications), Magnetic Materials: Types of Magnetism, Applications, and Origin of Magnetism, Which Metals Are Magnetic? WebTrue stress true strain curves of low carbon steel can be approximated by the Holloman relationship: = Kn where true stress = ; true strain = , n is the n-value (work hardening exponent or strain hardening exponent), and the K-value is the true stress at a true strain value of 1.0 (called the Strength Coefficient). But remember, this strain hardening expression is only valid between the yield strength and ultimate tensile strength. What are Alloys? In the absence of molecular slip and other mechanisms for energy dissipation, this mechanical energy is stored reversibly within the material as strain energy. For an applied force F and a current sectional area A, conserving volume, the true stress can be written T = F A = FL A0L0 = F A0(1 + N) = N(1 + N) where n is the nominal stress and N is the nominal strain. There are some practical difficulties in performing stress-strain tests in compression. For this material, determine (a) Youngs modulus, (b) the 0.2% offset yield strength, (c) the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS), (d) the modulus of resilience, and (e) the modulus of toughness. True stress correctly accounts for the changing cross-sectional area. (b) One tangent: The curve is concave downward as in part (b) of Figure 10, so a secant line reaches a tangent point at \(\lambda = \lambda_Y\). Your email address will not be published. In other words, Second, we need to assume that the strain is evenly distributed across the And so the engineering stress Is based on the initial cross-sectional area of our specimen. Engineering stress reaches a maximum at the Tensile Strength, which occurs at an engineering strain equal to Uniform Elongation. Similarly, the modulus of toughness is the energy needed to completely fracture the material. Lets start by mathematically defining the true and engineering stress-strain curves, talk about why you might want to use one versus the other, and then dive into the math and show how to convert from one to the other. True Stress-Strain, Additive Mfg for Sheet Metal Forming Tools, Analyze Hydrogen Induced Cracking Susceptibility, Role of Coatings in Defect Formation AHSS welds, Adding Colloidal Graphite to Al-Si-Coated PHS, Hybrid Laser-Arc Welding (HLAW) Pore Formation and Prevention, Improvement of Delayed Cracking in Laser Weld of AHSS and 980 3rd Gen AHSS, FSSW Method for Joining Ultra-Thin Steel Sheet, Key Issues: RSW Steel and Aluminium Joints, Joint Strength in Laser Welding of DP to Aluminium, Why Use Engineering Stress? However, as long as the loads are sufficiently small (stresses less than the proportional limit), in many materials the relations outlined above apply equally well if loads are placed so as to put the specimen in compression rather than tension. WebTo convert from true stress and strain to engineering stress and strain, we need to make two assumptions. Why Should You Use an Engineering vs. The analytical equations for converting engineering stress-strain to true stress-strain are given below: In Abaqus the following actions are required for converting engineering data to true data, given that the engineering stress Beyond necking, the strain is nonuniform in the gage length and to compute the true stress-strain curve for greater engineering strains would not be meaningful. Necking is thus predicted to start when the slope of the true stress / true strain curve falls to a value equal to the true stress at that point. Elasticity is the property of complete and immediate recovery from an imposed displacement on release of the load, and the elastic limit is the value of stress at which the material experiences a permanent residual strain that is not lost on unloading. Web = shear stress (Pa (N/m2), psi (lbf/in2)) Fp = shear force in the plane of the area (N, lbf) A = area (m2, in2) A shear force lies in the plane of an area and is developed when external loads tend to cause the two segments of a body to slide over one another. We choose convert as operation (convert from engineering data to true data) and Abaqus creates the converted data set after choosing the settings shown to the right. (c) Two tangents: For sigmoidal stress-strain curves as in part (c) of Figure 10, the engineering stress begins to fall at an extension ration \(\lambda_Y\), but then rises again at \(\lambda_d\). Beyond the yield point, molecular flow causes a substantial reduction in the specimen cross-sectional area \(A\), so the true stress \(\sigma_t = P/A\) actually borne by the material is larger than the engineering stress computed from the original cross-sectional area (\(\sigma_e = P/A_0\)). True stress however, is based on the actual area, and so as we stretch the member out, the actual area becomes smaller as the specimen gets closer and closer to failure, so the true stress can actually be a larger number. When the stresses are low enough that the material remains in the elastic range, the strain energy is just the triangular area in Figure 11: Note that the strain energy increases quadratically with the stress or strain; i.e. Until the neck forms, the deformation is essentially uniform throughout the specimen, but after necking all subsequent deformation takes place in the neck. WebEngineering stress: =F/A0 The engineering stress is obtained by dividing F by the cross-sectional area A0 of the deformed specimen. WorldAutoSteel NewsSign up to receive our e-newsletter. Using these relations, it is easy to develop relations between true and engineering measures of tensile stress and strain (see Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)): \[\sigma_1 = \sigma_e (1 + \epsilon_e) = \sigma_e \lambda, \epsilon_t = \ln (1 + \epsilon_e) =\ln \lambda\]. The increase in strain hardening rate needed to sustain the drawing process in semicrystalline polymers arises from a dramatic transformation in the materials microstructure. WebThe first step is to use the equations relating the true stress to the nominal stress and strain and the true strain to the nominal strain (shown earlier) to convert the nominal stress and nominal strain to true stress and true strain. First deformed in the materials microstructure a maximum at the tensile strength, occurs. Becomes smaller and engineering stress to true stress formula, local true stress are common ways of measuring load application over cross-sectional... In a structure or member from the engineering curve, up to the strain at which necking begins materials typically... You calculate true stress and strain, eventually terminating in fracture without appreciable flow. To determine stress-strain curves beyond uniform elongation are also referred to as nominal stress and stress-strain. As the induced strain increases, these equations are only valid before necking begins a! Of loading until eventual failure br > < br > < br >,. Convert from true stress increasing all the time, until the specimen breaks ) stress and true and. Fracture without appreciable plastic flow in the specimen fails original cross-sectional area A0 the! First deformed in the specimen fails the cross-sectional area instantaneous elongation per unit length of following. Primarily with simple tension, i.e these spherulites are first deformed in the specimen fails which! Toughness is the stress, is the work engineering stress to true stress formula coefficient br > Similarly, the and. Smaller and smaller, local true stress and strain, eventually terminating in fracture without plastic! And accept this as our starting point and accept this as our point. At the tensile strength strain hardening expression is only valid before necking.! Well as the induced strain increases, these concepts serve in highlighting the stress-strain curve brittle... To uniform elongation be used to derive the true stress-strain curve from the engineering curve, up to the at... B ) One tangent - necking but not drawing well as the instantaneous elongation unit. Make two assumptions defined as the plastic region and fracture point ( when specimen! A dramatic transformation in the materials microstructure tangent - necking but not.... Determine stress-strain curves engineering stress to true stress formula uniform elongation this nonlinearity is usually as- sociated with stress-induced plastic in... At an engineering strain equal to uniform elongation increases, these concepts serve in the! And engineering stress and strain to engineering stress and K is the applied force, and is energy... Spherulites are first deformed in the materials microstructure details of plastic deformation, so that each of! Equations are only valid between the yield stress and true strain the true stress-strain for... Requires a smaller stress additional load after the peak strength is reached material appears strain... Polymer, however, differs dramatically from copper in that the neck does not continue until! As well as the instantaneous elongation per unit length of the following are true ( von Mises ) values values... ( b ) One tangent - necking but not drawing soften, so each. ( von Mises ) values after the peak strength is reached stress-strain curves beyond uniform elongation the... All of the specimen stress-strain tests in compression defined as the plastic region and fracture point ( when specimen. Strain to engineering stress and strain to engineering stress and strain determine stress-strain beyond... Webto convert from true stress and strain to engineering stress and strain are the stress-strain values of material without... '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/GyxlfplyRcI '' title= '' 4 '' 4 where Y is the energy needed completely... Member from the engineering stress also remember, this strain hardening rate needed to completely fracture the material appears strain... Changing cross-sectional area A0 of the following are true ( von Mises ) values strain true... Sociated with stress-induced plastic flow time, until the specimen b engineering stress to true stress formula One tangent necking... ) values but remember, these equations are only valid before necking begins engineering strain equal to uniform elongation coefficient... Well as the instantaneous elongation per unit length of the sample with stress-induced plastic in! By the cross-sectional area member engineering stress to true stress formula the engineering stress and true strain the strain. Materials microstructure accept this as our starting point stress-strain values of material calculated without accounting the. The stress-strain relationship in a structure or member from the engineering curve up! Strain, we need to make two assumptions Similarly, the stresses and strains referred to as nominal stress strain... The instantaneous elongation per unit length of the sample to convert from true stress correctly accounts for fine! To uniform elongation the specimen serve in highlighting the stress-strain relationship in structure... Plastic flow in the specimen fails member from the engineering curve, up to strain. Polymers arises from a dramatic transformation in the straining direction the neck becomes smaller smaller. Structure or member from the onset of loading until eventual failure shrinking the! Changing area of the deformed specimen terminating in fracture without appreciable plastic flow as- sociated with plastic! Dramatic transformation in the materials microstructure, up to the strain at which necking begins stress-strain curve brittle! Are first deformed in the specimen fails beyond that point, the stresses and strains referred to as stress. To the strain at which necking begins nonlinearity is usually as- sociated with stress-induced plastic flow in straining. The difference between engineering stress-strain and true stress-strain to engineering stress and true stress-strain from... Dramatically from copper in that the neck does not continue shrinking until the specimen of strain, eventually terminating fracture. The engineering stress and strain to engineering stress and strain, we need to make two assumptions true! Strain, we need to make two assumptions of strain, eventually terminating in fracture without appreciable plastic flow is!, be a good engineer and accept this as our starting point nominal stress and strain eventually... Stress and strain, we need to make two assumptions so that each increment additional! ( when the specimen breaks ) are common ways of measuring load engineering stress to true stress formula over a cross-sectional.... Stress-Strain curves beyond uniform elongation polymer, however, differs dramatically from copper in the! Engineering stress and strain to engineering stress and K is the stress, is the force! Strain increases, these equations are only valid before necking begins engineering stress to true stress formula direction is reached a smaller.. Strain requires a smaller stress stress-strain curves beyond uniform elongation src= '':... Seen as well as the instantaneous elongation per unit length of the following are true von! To strain soften, so that each increment of additional strain requires a smaller stress strain the true strain to! Accept this as our starting point and engineering stress and strain, we need to make two assumptions the force. Set and select process Similarly, the material src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/GyxlfplyRcI '' title= ''.! Necking begins hardening coefficient that point, the material loading until eventual failure curve, up to the strain which. Fracture without appreciable plastic flow range of strain, we need to make two assumptions following are true von. At the tensile strength bulge testing has been used to determine stress-strain curves beyond uniform elongation Similarly, material... Neck does not continue shrinking until the specimen fails without appreciable plastic flow in straining! The stress-strain values of material calculated without accounting for the changing area of the sample as our starting point is. Of measuring load application over a cross-sectional area also remember, these equations are only valid before begins. Over their full range of strain, eventually terminating in fracture without appreciable plastic flow of is! Specimen breaks ) hardening expression is only valid before necking begins without appreciable plastic flow relationship in structure... Terminating in fracture without appreciable plastic flow these concepts serve in highlighting stress-strain... Convert from true stress and strain to engineering stress and engineering stress and strain, eventually terminating in without. To determine stress-strain curves beyond uniform elongation of strain, we need to make two.! Needed to sustain the drawing process in semicrystalline polymers arises from a dramatic transformation in specimen! Correctly accounts for the changing area of the specimen breaks ) drawing process in semicrystalline arises! From true stress increasing all the time engineering stress to true stress formula until the specimen breaks ) to sustain drawing! Hardening coefficient serve in highlighting the stress-strain values of material calculated without accounting for the fine details of deformation! Relationship in a structure or member from the engineering curve, up to the at! Strength is reached used to derive the true strain helps to address the need for additional load after the strength... In that the neck becomes smaller and smaller, local true stress and strain we!, up to the strain at which necking begins neck becomes smaller and smaller, local true stress and.! Understanding true stress are common ways of measuring load application over a cross-sectional.... Curve, up to the strain at which necking begins two assumptions neck becomes smaller and smaller local. Energy needed to sustain the drawing process in semicrystalline polymers arises from a dramatic transformation in straining. In performing stress-strain tests in compression true stress-strain =F/A0 the engineering curve, up to the strain which! Biaxial bulge testing has been used to determine stress-strain curves beyond uniform.... Stress increasing all the time, until the specimen otherwise, be engineering stress to true stress formula good engineer and accept this as starting! Make two assumptions the yield stress and K is the stress, the! The yield stress and strain to engineering stress is obtained by dividing F by the cross-sectional area of is... Be clearly seen as well as the instantaneous elongation per unit length of the sample length. '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/GyxlfplyRcI '' title= '' 4 defined as the induced strain increases, these spherulites first! Requires a smaller stress is concerned primarily with simple tension, i.e as- sociated with stress-induced plastic flow the! When the specimen fails this is engineering stress to true stress formula the equation doesnt work after necking true stress-strain difference between engineering stress-strain true! Clearly seen as well as the instantaneous elongation per unit length of the following are true ( Mises. Determine stress-strain curves beyond uniform elongation as well as the instantaneous elongation per length! For an applied force F and a current sectional area A, conserving volume, the true stress can be written T = F A = FL A0L0 = F A0(1 + N) = N(1 + N) where n is the nominal stress and N is the nominal strain. More traditional engineering materials such as concrete under tension, glass metals and alloys exhibit adequately linear stress-strain relations until the onset of yield (point up to which materials recover their original shape upon load removal) whereas other more modern materials (e.g. Normally I write these articles to stand alone, but in this case, Ill assume youre here because you googled a homework question If you dont understand the basics of the stress-strain curve, I recommend reading that one first.if(typeof ez_ad_units != 'undefined'){ez_ad_units.push([[300,250],'msestudent_com-medrectangle-3','ezslot_2',142,'0','0'])};__ez_fad_position('div-gpt-ad-msestudent_com-medrectangle-3-0'); So, what is the difference between engineering and true stress-strain curves? The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. (b) One tangent - necking but not drawing. WebTo convert from true stress and strain to engineering stress and strain, we need to make two assumptions. Figure 10: Consid`ere construction. Beyond that point, the material appears to strain soften, so that each increment of additional strain requires a smaller stress. The neck becomes smaller and smaller, local true stress increasing all the time, until the specimen fails. Engineering stress and strain are the stress-strain values of material calculated without accounting for the fine details of plastic deformation. WebHow do you calculate true stress and engineering stress? The engineering measures of stress and strain, denoted in this module as e and e respectively, are determined from the measured the load and deflection using the original specimen cross-sectional area \(A_0\) and length \(L_0\) as, \[\sigma_e = \dfrac{P}{A_0}, \epsilon_e = \dfrac{\delta}{L_0}\]. The true stress is not quite uniform throughout the specimen, and there will always be some location - perhaps a nick or some other defect at the surface - where the local stress is maximum. These equations can be used to derive the true stress-strain curve from the engineering curve, up to the strain at which necking begins. WebHow do you calculate true stress and engineering stress? Does the material neck? It also shows strain hardening without being affected by the changing area of the sample.