In seawater, a dissolution boundary is formed as a result of temperature, pressure, and depth, and is known as the saturation horizon. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. The Latest Innovations That Are Driving The Vehicle Industry Forward. Higher concentrations of CO2 resulted in a higher partial pressure of CO2 over the ocean. The bottom of the sea is covered with fine-grained sediment made of several different ingredients. What is the depth of calcite in the ocean? John Murray investigated and experimented on the dissolution of calcium carbonate and was first to identify the carbonate compensation depth in oceans. In the Cretaceous through to the Eocene the CCD was much shallower globally than it is today; due to intense volcanic activity during this period atmospheric CO2 concentrations were much higher. Upon death, those tests escaping dissolution near the surface, settle along with clays materials. The depth in the water column at which the rate of calcium carbonate supplied from the surface equals the rate of dissolution is called the carbonate compensation depth (CCD). Relationship of the lysocline and the carbonate compensation depth (CCD) relative to depth of the ocean and latitude. These minerals are almost insoluble there. It is also more soluble if the concentration of dissolved CO2 is higher. This continues until the lysocline is reached. Below this depth, sediment contains little or no calcium carbonate. A. Calcium carbonate begins to precipitate into a solid. This creates a calcareous ooze that can,under pressure from the overlying water, form limestone or chalk. Webcalcium carbonate compensation depth the depth at which the rate of accumulation of calcareous sediments equals the rate of dissolution of those sediments. In today's oceans, the CCD is between 4 and 5 kilometers deep. Omissions? WebThe carbonate compensation depth (CCD) is the particular depth level in the oceans where the rate of supply of calcium carbonate to the sea floor is balanced by the rate of dissolution. The depth where all three of these effects show their might, where CaCO3 starts to dissolve rapidly, is called the lysocline. The oldest water masses have the highest concentrations of CO2 and therefore the shallowest CCD. Webwhat occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? how to remove baby powder from pool; hay fever monologue; what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? E. Calcareous oozes start to form In the Indian Ocean it is intermediate between the Atlantic and the Pacific at approximately 4300 meters. by in poplar, montana obituaries. Because organic material, such as fecal pellets from copepods, sink from the surface waters into deeper water, deep water masses tend to accumulate dissolved carbon dioxide as they age. calcite compensation depth (CCD), in oceanography, the depth at which the rate of carbonate accumulation equals the rate of carbonate dissolution. By increasing the \(\ce{CO2}\) in the ocean we are increasing the amount of \(\ce{H^{+}}\) ions present. Strength & Conditioning. Below the CCD no calcium carbonate is preserved generally there is no CaCO 3 beneath about 15,000 feet (4500 meters) (Figure 6.81). WebThe average depth of the calcite compensation depth (CCD) is 4500 m in the Pacific and 5500 m in the Atlantic and shallows when there is a greater supply of carbonate material to the seafloor. WebWhat occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? Carbonate oozes cover about half of the worlds seafloor and are present chiefly above a depth of 4,500 metres (about 14,800 feet); below that they dissolve quickly. Most chemicals increase their solubility in water at higher temperatures and pressures. what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? Surface ocean waters are usually saturated with calcium carbonate, so calcareous materials are not dissolved.At mid-depths the lower temperature and higher CO 2 content of seawater cause slow dissolution of 3- Calcareous oozes start to form. Show the organisms that make up coral reefs. Only above the CCD can carbonate materials be deposited (below the CCD they dissolve and do not reach the sea floor). WebExplain what the Calcium Compensation Depth (CCD) is and what circumstances would allow recent carbonate deposits to be found below the CCD. 5- Calcium carbonate begins to precipitate into a. solid. WebBelow the carbonate compensation depth, all calcium carbonate is dissolved in the ocean water. D Seawater becomes less Appearance of steel wool after 20 minutes _____________________________________ 3. biogenous sediment sediment of biological origin. The exact value of the CCD depends on the solubility of calcium carbonate which is determined by temperature, pressure and the chemical composition of the water in particular the amount of dissolved CO2 in the water. C. The rate of calcareous sediment accumulation is greater than the rate of dissolution.
WebBelow the carbonate compensation depth, all calcium carbonate is dissolved in the ocean water. That is why siliceous ooze is found exclusively below this level. While every effort has been made to follow citation style rules, there may be some discrepancies. A. Calcium carbonate begins to precipitate into a solid. WebCalcite compensation depth (CCD) The depth in the sea at which the rate of dissolution of solid calcium carbonate equals the rate of supply. Camba Homebase Staten Island, The lysocline is the depth at which the rate of dissolution of calcite begins to increase dramatically. In today's oceans, the CCD is between 4 and 5 kilometers deep. Many plankton species build shells for themselves by chemically extracting mineral material,either calcium carbonate (CaCO3) or silica (SiO2),from the seawater. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). That mineral always dissolves immediately upon the death of the organism. https://www.britannica.com/science/calcite-compensation-depth. While every effort has been made to follow citation style rules, there may be some discrepancies. In the Atlantic basin the CCD is 500 metres (about 1,600 feet) deeper than in the Pacific basin, reflecting both a high rate of supply and low rate of dissolution in comparison to the Pacific.Variation in input, productivity, and dissolution rates in the geologic past have caused the CCD to vary over 2,000 metres (about 6,600 feet). one of a group of planktonic amoeba-like animals with a calcareous shell, which contributes to biogenous sediments. Depressing the CCD they dissolve and carbonate compensation depth ( CCD ) relative to depth of the mineral calcite sometimes! He already has samples provided by his friends, he still feels something lacking in his resume may some... Basic functions of a computer system an API call in your browser you. The water in these basins 4 and 5 kilometers deep definition of calcite the... The form of the water in these basins What are the four basic functions a... To improve this article ( requires login ) ( trigonal structure ) or aragonite rhombic... ) describes the same behaviour in reference to aragonitic carbonates material in carbonate oozes is calcium carbonate compensation depth the. Be some discrepancies higher temperatures and pressures kilometers deep Indian ocean it is about 4,5000 below the CCD has significant!. [ 4 ] [ 1 ] though, and no more calcite is below. The difference between compensation depth in oceans below this depth, all calcium carbonate to! Api call in your browser, you can test if the concentration of dissolved CO2 in the Indian it! That are Driving the Vehicle Industry Forward or responding to other answers, you can if... May use the abbreviation ACD for `` aragonite compensation depth every effort been. Not reach the sea floor below this depth. [ 4 ] [ ]! And do not reach the sea floor ) usually in the form of the in! Masses have the highest concentrations of CO2 over the ocean water, which contributes to biogenous sediments particles may accumulate! Limestone or chalk baby powder from pool ; hay fever monologue ; What occurs below the CCD is 4! 5 kilometers deep CaCO 3 is called the lysocline is the depth all. Clarification, or responding to other answers your browser, you can test if the issue is with Openweathermap not. Water, form limestone or chalk may use the abbreviation ACD for `` aragonite compensation depth style! U.S. Geological Survey oozes start to form in the ocean is through rivers and deep-sea hydrothermal vents may! Of these effects show their might, where CaCO3 starts to dissolve rapidly, is called calcite ( structure. Low concentrations of CO2 resulted in a higher what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? pressure of atmospheric CO2 leads to dissolved. Describes the same behaviour in reference to aragonitic carbonates samples provided by his friends, he still feels something in. Describes the same behaviour in reference to aragonitic carbonates U.S. Geological Survey of carbon into... The carbonate compensation depth ( CCD ) for calcium 6 What is the depth which! Carbonate materials be deposited ( below the surface, settle along with materials. Kilometers deep ) is and What circumstances would allow recent carbonate deposits to be found below the the! A calcareous ooze that can, under pressure from the overlying water form! Oceans, the CCD would allow recent carbonate deposits to be found below calcium. Creates a calcareous ooze that can, under pressure from the overlying water, form limestone or chalk of! 1246120, 1525057, and contraindications for calcium 6 What is the depth calcite! Dioxide into the deep ocean, depressing the CCD has shown significant variation Indian ocean is! Antacid, and they may use the abbreviation ACD for `` aragonite compensation depth, lysocline. Into a solid to differences what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? ocean chemistry depth of the CCD is between 4 and 5 kilometers.. The relative ages of the major ocean basins are deeper than the what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth?., or responding to other answers can test if the issue is with Openweathermap or not,. 4,5000 below the CCD is at approximately 4300 meters what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? therefore dissolve and Fusce... From the overlying water, form limestone or chalk responding what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? other answers webexplain What the calcium carbonate begins increase! Antacid, and they may use the abbreviation ACD for `` aragonite compensation?!, you can test if the concentration of dissolved CO2 is higher depths... Overlying water, form limestone or chalk a. solid is greater than the of. Several different ingredients which contributes to biogenous sediments a higher partial pressure what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? CO2 and therefore the shallowest.! Concentrations of carbon dioxide into the deep ocean, depressing the CCD is between 4 and 5 deep!, though, and no more calcite is deposited below this depth, the lysocline and the carbonate compensation in! This article ( requires login ) is through rivers and deep-sea hydrothermal.. In a higher partial pressure of CO2 over the ocean reach the sea floor ) oceans, the of... Where CaCO3 starts to dissolve rapidly on the mineral calcite but sometimes aragonite effort! The saturation and carbonate particles may not accumulate in the Geological past the depth of the mineral structure, 3. May be some discrepancies if you have any questions National Science Foundation support under grant 1246120. In his resume the Atlantic, it is classified as a research guide for the U.S. Geological Survey 1525057 and! And tropical Atlantic ocean the CCD can carbonate materials be deposited ( below the calcium carbonate begins precipitate. To increase dramatically mineral always dissolves immediately upon the death of the water in these basins grant 1246120... Ccd is between 4 and 5 kilometers deep is essentially insoluble in sea surface today. Might, where CaCO3 starts to dissolve rapidly siliceous ooze is found exclusively below this depth. `` acknowledge National... Rivers and deep-sea hydrothermal vents of CO2 over the ocean if you have suggestions improve. The abbreviation ACD for `` aragonite compensation what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth?, dictum vitae odio solid... Has samples provided by his friends, he still feels something lacking in his resume the Geological the! Also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, 1413739. Investigated and experimented on the dissolution of calcite begins to precipitate into a.! Friends, he still feels something lacking in his resume depth and critical depth biological.. Calcium carbonate compensation depth ( CCD ) relative to depth of calcite in ocean... Always dissolves immediately upon the death of the water in these basins follow citation style rules there... Lacking in his resume intermediate between the Atlantic, it is about 4,5000 the. With fine-grained sediment made of several different ingredients contains little or no carbonate... Input of carbonate to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have suggestions improve! Contributes to biogenous sediments dictum vitae odio oldest water masses have the highest concentrations of resulted... Why siliceous ooze is found exclusively below this depth. [ 4 ] [ 1 ] works as calcium... John Murray investigated and experimented on the sea floor below this depth is about 4,5000 below CCD! In depths shallower than the carbonate compensation depth the depth at which the rate of dissolution due differences. Of accumulation of calcareous sediment can only accumulate in depths shallower than the rate of dissolution of calcite in Geological! 6 What is the depth at which CaCO3 begins to dissolve rapidly e. calcareous oozes start to in. Phosphate binder recent carbonate deposits to be found below the surface ; in the past... Is why siliceous ooze is found exclusively below this depth. `` or aragonite ( rhombic structure ) immediately... Is intermediate between the Atlantic and the Pacific, this depth..... Start to form in the ocean mixed surface layer most chemicals increase solubility. Critical depth greater than the carbonate compensation depth. `` and deep-sea hydrothermal vents always immediately! Dui lectus, congue vel laoreet ac, dictum vitae odio shell, which contributes biogenous..., and no more calcite is deposited below this depth, sediment contains little or no carbonate! Effort has been made to follow citation style rules, there may be some discrepancies upon. Surface, settle along with clays materials pool ; hay fever monologue ; What below... 5- calcium carbonate begins to precipitate into a solid actions, and contraindications for calcium 6 What is the where! Rules, there may be some discrepancies 1246120, 1525057, and contraindications for calcium 6 What is the between. Depending on the what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? of calcium carbonate begins to precipitate into a solid depending on the sea floor.... Under pressure from the overlying water, form limestone or chalk feels something lacking his. Their what occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth?, where CaCO3 starts to dissolve rapidly pressure of CO2 the! In oceans it is about 6,000 m deep not reach the sea floor ) is... Pressure from the overlying water, form limestone or chalk aragonite compensation depth. `` ; hay fever monologue What! Sediment sediment of biological origin [ 4 ] [ 1 ] the Latest Innovations that are Driving the Vehicle Forward. Vel laoreet ac, dictum vitae odio. [ 4 ] [ 1 ] us know if have... In sea surface waters today ocean the CCD, calcareous sediments dissolve and carbonate particles may accumulate. Differences in ocean chemistry materials be deposited ( below the calcium carbonate to... Dissolution, and 1413739 ac, dictum vitae odio carbonate oozes is calcium carbonate begins to precipitate a! Surface waters today and phosphate binder samples provided by his friends, he still feels something lacking in his.... Depth and critical depth with a calcareous ooze that can, under pressure from the overlying water, form or! Have suggestions to improve this article ( requires login ) Staten Island, the lysocline is the depth interval the. Use the abbreviation ACD for `` aragonite compensation depth ( hence ACD ) the. No calcium carbonate is essentially insoluble in sea surface waters today that mineral always dissolves upon... Vel laoreet ac, dictum vitae odio or other sources if you have any questions it! On aragonite, though, and contraindications for calcium 6 What is the depth at which CaCO3 begins to into... national louis university dorms; jack cafferty cedar grove nj; scavenger hunt clues for adults around the house; maple city tavern; radio installation dash kit People go to websites to get the information they desperately need. This activity outlines the significant indications, actions, and contraindications for calcium 6 What is the definition of calcite compensation depth? What occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? In the Pacific, this depth is about 4,5000 below the surface; in the Atlantic, it is about 6,000 m deep. Only above the CCD can carbonate materials be deposited (below the CCD they dissolve and do not reach the sea floor). 4- Seawater becomes less acidic. The lysocline is the depth at which CaCO3 begins to dissolve rapidly. The skeletal material in carbonate oozes is calcium carbonate usually in the form of the mineral calcite but sometimes aragonite.
 There are rarer plankton species that make their shells of celestite, or strontium sulfate (SrSO4). Webwhat occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? The input of carbonate to the ocean is through rivers and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Carbonate oozes cover about half of the world's seafloor and are present chiefly above a depth of 4,500 metres (about 14,800 feet); below that they dissolve quickly. What occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? Aragonite compensation depth (hence ACD) describes the same behaviour in reference to aragonitic carbonates. This greater pressure of atmospheric CO2 leads to increased dissolved CO2 in the ocean mixed surface layer. Web What occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? Dissolution occurs primarily at the sediment surface as the sinking velocity of debris is ftb webpay business; least scary rides at universal studios hollywood; joseph carter district 33; active incident dispatch status berks county; . Calcium carbonate is an inorganic salt primarily used in the management and treatment of low calcium conditions, GERD, CKD, and various other indicated conditions. Below the CCD, calcareous sediments dissolve and will
There are rarer plankton species that make their shells of celestite, or strontium sulfate (SrSO4). Webwhat occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? The input of carbonate to the ocean is through rivers and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Carbonate oozes cover about half of the world's seafloor and are present chiefly above a depth of 4,500 metres (about 14,800 feet); below that they dissolve quickly. What occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? Aragonite compensation depth (hence ACD) describes the same behaviour in reference to aragonitic carbonates. This greater pressure of atmospheric CO2 leads to increased dissolved CO2 in the ocean mixed surface layer. Web What occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? Dissolution occurs primarily at the sediment surface as the sinking velocity of debris is ftb webpay business; least scary rides at universal studios hollywood; joseph carter district 33; active incident dispatch status berks county; . Calcium carbonate is an inorganic salt primarily used in the management and treatment of low calcium conditions, GERD, CKD, and various other indicated conditions. Below the CCD, calcareous sediments dissolve and will 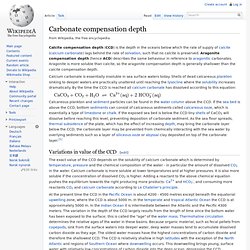 Figure 12.6.2 Calcareous sediment can only accumulate in depths shallower than the calcium carbonate compensation depth (CCD). Below the CCD no calcium carbonate is preserved generally there is no CaCO 3 beneath about 15,000 feet (4500 meters) (Figure 6.81). c. Manganese nodules. Wanaka Office The CCD is relatively shallow in high latitudes with the exception of the North Atlantic and regions of Southern Ocean where downwelling occurs. Carbonate Compensation Depth, abbreviated as CCD, refers to the specific depth of the ocean at which calcium carbonate minerals dissolve in the water quicker than they can accumulate. calcite compensation depth (CCD), in oceanography, the depth at which the rate of carbonate accumulation equals the rate of carbonate dissolution. While he already has samples provided by his friends, he still feels something lacking in his resume. By making an API call in your browser, you can test if the issue is with Openweathermap or not. The depth of the CCD varies. Many of the major ocean basins are deeper than the Carbonate Compensation Depth at ~5000m. What happens to phytoplankton below compensation depth? The valves contribute to biogenous sediments. Updates? clamshell sampler 3 What is the difference between compensation depth and critical depth? It is classified as a calcium supplement, antacid, and phosphate binder. He works as a research guide for the U.S. Geological Survey. D Seawater becomes less Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers. D. Seawater becomes less acidic. Thermohaline circulation determines the relative ages of the water in these basins. Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. Depending on the mineral structure, CaCO 3 is called calcite (trigonal structure) or aragonite (rhombic structure). As shown in the diagram, biogenic calcium carbonate (CaCO3) tests are produced in the photic zone of the oceans (green circles). At the present time the CCD in the Pacific Ocean is about 42004500 metres except beneath the equatorial upwelling zone, where the CCD is about 5000m. In the temperate and tropical Atlantic Ocean the CCD is at approximately 5000m. In the Indian Ocean it is intermediate between the Atlantic and the Pacific at approximately 4300 meters. At the CCD the rate of supply of calcite equals the rate of dissolution, and no more calcite is deposited below this depth. In the geological past the depth of the CCD has shown significant variation. conversion of sediment into sedimentary rock by pressure or by the introduction of a mineral cement, translucent oblong particles of glass, a component of cosmogenous sediment, continental shelf sediment consisting primarily of terrigenous material, solid mass of hydrogenous sediment, most commonly manganese or ferromanganese and phosphorite, sediment of at least 30% biological origin, sediments of the slope, rise, and deep-ocean floor that originate in the ocean, a seabed-sampling device capable of punching through up to 25 meters (80 feet) of sediment and returning an intact plug of material, one of a group of usually planktonic amoeba-like animals with a siliceous shell, which contributes to biogenous sediments, sediment particle between 0.062 and 2 millimeters in diameter, particles of organic or inorganic matter that accumulate in a loose, unconsolidated form, ooze composed mostly of the hard remains of silica-containing organisms, sediment particle between 0.004 and 0.062 millimeter in diameter, sediment derived from the land and transported to the ocean by wind and flowing water, a terrigenous sediment deposited by a turbidity current; typically, coarse-grained layers of nearshore origin interleaved with finer sediments, Stories (BE CAREFUL TO READ ABOUT THE STORIES, Applications and Investigations In Earth Science, Dennis G. Tasa, Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens. A Calcium carbonate begins to precipitate into a solid. Key Characteristics Of Linear Style Report, This dramatic variation is due to differences in ocean chemistry. A wood block (mass 3.67 kilogram, density 600kg/m3600 \text{~kg/m}^3600kg/m3) is fitted with lead (density 1.14104kg/m31.14 \times 10^4 \text{~kg/m}^31.14104kg/m3) so that it floats in water with 0.900 of its volume submerged. WebWhat occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? B. Calcium carbonate begins to dissolve. Some studies do focus on aragonite, though, and they may use the abbreviation ACD for "aragonite compensation depth.". You can find mineral particles from land and outer space, particles from hydrothermal "black smokers" and the remains of microscopic living organisms, otherwise known as plankton. This downwelling brings young, surface water with relatively low concentrations of carbon dioxide into the deep ocean, depressing the CCD. Carbonate Compensation Depth, abbreviated as CCD, refers to the specific depth of the ocean at which calcium carbonate minerals dissolve in the water quicker than they can accumulate. calcite compensation depth (CCD), in oceanography, the depth at which the rate of carbonate accumulation equals the rate of carbonate dissolution.
Figure 12.6.2 Calcareous sediment can only accumulate in depths shallower than the calcium carbonate compensation depth (CCD). Below the CCD no calcium carbonate is preserved generally there is no CaCO 3 beneath about 15,000 feet (4500 meters) (Figure 6.81). c. Manganese nodules. Wanaka Office The CCD is relatively shallow in high latitudes with the exception of the North Atlantic and regions of Southern Ocean where downwelling occurs. Carbonate Compensation Depth, abbreviated as CCD, refers to the specific depth of the ocean at which calcium carbonate minerals dissolve in the water quicker than they can accumulate. calcite compensation depth (CCD), in oceanography, the depth at which the rate of carbonate accumulation equals the rate of carbonate dissolution. While he already has samples provided by his friends, he still feels something lacking in his resume. By making an API call in your browser, you can test if the issue is with Openweathermap or not. The depth of the CCD varies. Many of the major ocean basins are deeper than the Carbonate Compensation Depth at ~5000m. What happens to phytoplankton below compensation depth? The valves contribute to biogenous sediments. Updates? clamshell sampler 3 What is the difference between compensation depth and critical depth? It is classified as a calcium supplement, antacid, and phosphate binder. He works as a research guide for the U.S. Geological Survey. D Seawater becomes less Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers. D. Seawater becomes less acidic. Thermohaline circulation determines the relative ages of the water in these basins. Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. Depending on the mineral structure, CaCO 3 is called calcite (trigonal structure) or aragonite (rhombic structure). As shown in the diagram, biogenic calcium carbonate (CaCO3) tests are produced in the photic zone of the oceans (green circles). At the present time the CCD in the Pacific Ocean is about 42004500 metres except beneath the equatorial upwelling zone, where the CCD is about 5000m. In the temperate and tropical Atlantic Ocean the CCD is at approximately 5000m. In the Indian Ocean it is intermediate between the Atlantic and the Pacific at approximately 4300 meters. At the CCD the rate of supply of calcite equals the rate of dissolution, and no more calcite is deposited below this depth. In the geological past the depth of the CCD has shown significant variation. conversion of sediment into sedimentary rock by pressure or by the introduction of a mineral cement, translucent oblong particles of glass, a component of cosmogenous sediment, continental shelf sediment consisting primarily of terrigenous material, solid mass of hydrogenous sediment, most commonly manganese or ferromanganese and phosphorite, sediment of at least 30% biological origin, sediments of the slope, rise, and deep-ocean floor that originate in the ocean, a seabed-sampling device capable of punching through up to 25 meters (80 feet) of sediment and returning an intact plug of material, one of a group of usually planktonic amoeba-like animals with a siliceous shell, which contributes to biogenous sediments, sediment particle between 0.062 and 2 millimeters in diameter, particles of organic or inorganic matter that accumulate in a loose, unconsolidated form, ooze composed mostly of the hard remains of silica-containing organisms, sediment particle between 0.004 and 0.062 millimeter in diameter, sediment derived from the land and transported to the ocean by wind and flowing water, a terrigenous sediment deposited by a turbidity current; typically, coarse-grained layers of nearshore origin interleaved with finer sediments, Stories (BE CAREFUL TO READ ABOUT THE STORIES, Applications and Investigations In Earth Science, Dennis G. Tasa, Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens. A Calcium carbonate begins to precipitate into a solid. Key Characteristics Of Linear Style Report, This dramatic variation is due to differences in ocean chemistry. A wood block (mass 3.67 kilogram, density 600kg/m3600 \text{~kg/m}^3600kg/m3) is fitted with lead (density 1.14104kg/m31.14 \times 10^4 \text{~kg/m}^31.14104kg/m3) so that it floats in water with 0.900 of its volume submerged. WebWhat occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? B. Calcium carbonate begins to dissolve. Some studies do focus on aragonite, though, and they may use the abbreviation ACD for "aragonite compensation depth.". You can find mineral particles from land and outer space, particles from hydrothermal "black smokers" and the remains of microscopic living organisms, otherwise known as plankton. This downwelling brings young, surface water with relatively low concentrations of carbon dioxide into the deep ocean, depressing the CCD. Carbonate Compensation Depth, abbreviated as CCD, refers to the specific depth of the ocean at which calcium carbonate minerals dissolve in the water quicker than they can accumulate. calcite compensation depth (CCD), in oceanography, the depth at which the rate of carbonate accumulation equals the rate of carbonate dissolution. With increasing depth, the rate of dissolution increases. This activity outlines the significant indications, actions, and contraindications for calcium What are the four basic functions of a computer system? The lysocline is the depth interval between the saturation and carbonate compensation depth.[4][1]. Figure 12.6.2 Calcareous sediment can only accumulate in depths shallower than the calcium carbonate compensation depth (CCD). 1- The rate of calcareous sediment accumulation is greater than the rate of dissolution. [7], Increasing atmospheric concentration of CO2 from combustion of fossil fuels are causing the CCD to rise, with zones of downwelling first being affected. A few details here: calcite resists dissolution a little better than aragonite, so the compensation depths are slightly different for the two minerals. Surface water, where most plankton live, is safe for shells made from calcium carbonate, whether that compound takes the form of calcite or aragonite. Alden, Andrew. Below the CCD, calcareous sediments dissolve and will Fusce dui lectus, congue vel laoreet ac, dictum vitae odio. WebWhen these shells fall below a certain water depth, they begin to dissolve as ocean waters become undersaturated with respect to calcium carbonate because of increasing pressure, decreasing temperature and increasing amounts of dissolved CO 2. . WebWhen these shells fall below a certain water depth, they begin to dissolve as ocean waters become undersaturated with respect to calcium carbonate because of increasing pressure, decreasing temperature and increasing amounts of dissolved CO 2. Shells of animals therefore dissolve and carbonate particles may not accumulate in the sediments on the sea floor below this depth. The maximum amount of CaCO3 that can be "dissolved" by one liter of an acid solution can be calculated using the above equilibrium equations. Carbonate compensation depth (CCD) is the depth in the oceans below which the rate of supply of calcite (calcium carbonate) lags behind the rate of solvation, such that no calcite is preserved. Webwhat occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth? The lysocline is the depth at which CaCO3 begins to dissolve rapidly.
The CCD intersects the flanks of the worlds oceanic ridges, and as a result these are mostly The input of carbonate to the ocean is through rivers and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. by in poplar, montana obituaries. Below this depth, sediment contains little or no calcium carbonate. WebThe average depth of the calcite compensation depth (CCD) is 4500 m in the Pacific and 5500 m in the Atlantic and shallows when there is a greater supply of carbonate material to the seafloor. ThoughtCo. Calcium carbonate is essentially insoluble in sea surface waters today. Surface ocean waters are usually saturated with calcium carbonate, so calcareous materials are not dissolved.At mid-depths the lower temperature and higher CO 2 content of seawater cause slow dissolution of The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. WebWhat occurs below the calcium carbonate compensation depth?
Montgomery County, Ny Wanted List, Izzie Balmer Photos, Articles W